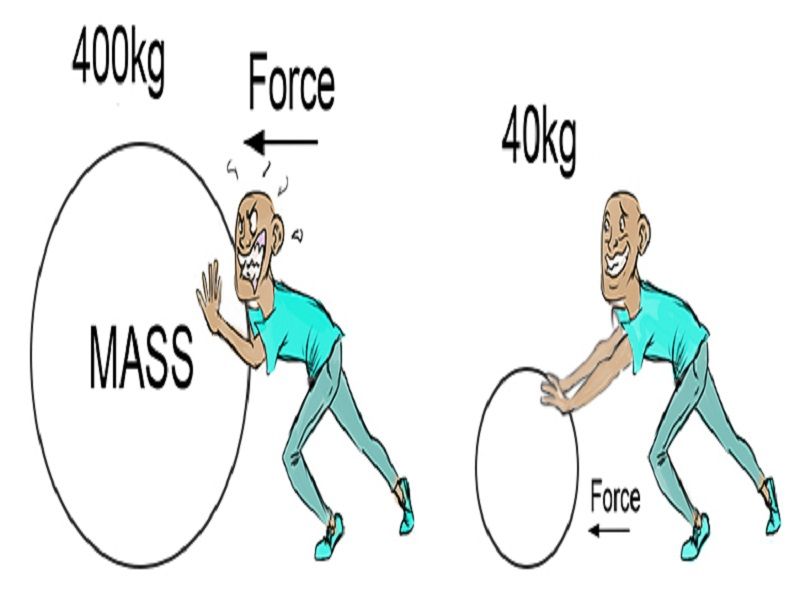
Newton's Second Law In Component Form
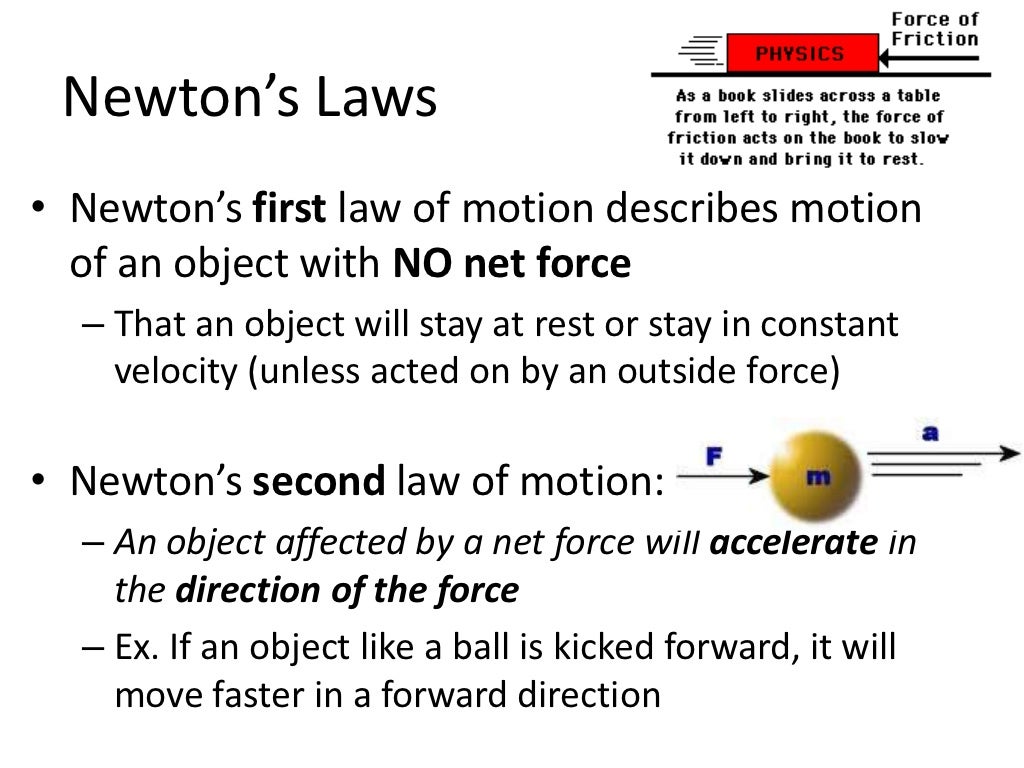
Newton's Second Law In Component Form - According to newton’s second law: Web component form of newton’s second law. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web we have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in (figure). Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to the mass of that body times its rate of acceleration. Web this allows us to calculate, correspondingly, the x component and y component of the acceleration vector of our system. We have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in. Web (a) two students push a stalled car. Web newton's second law of motion states the acceleration of an object is dependent on the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. Web si unit of force is newton (n).
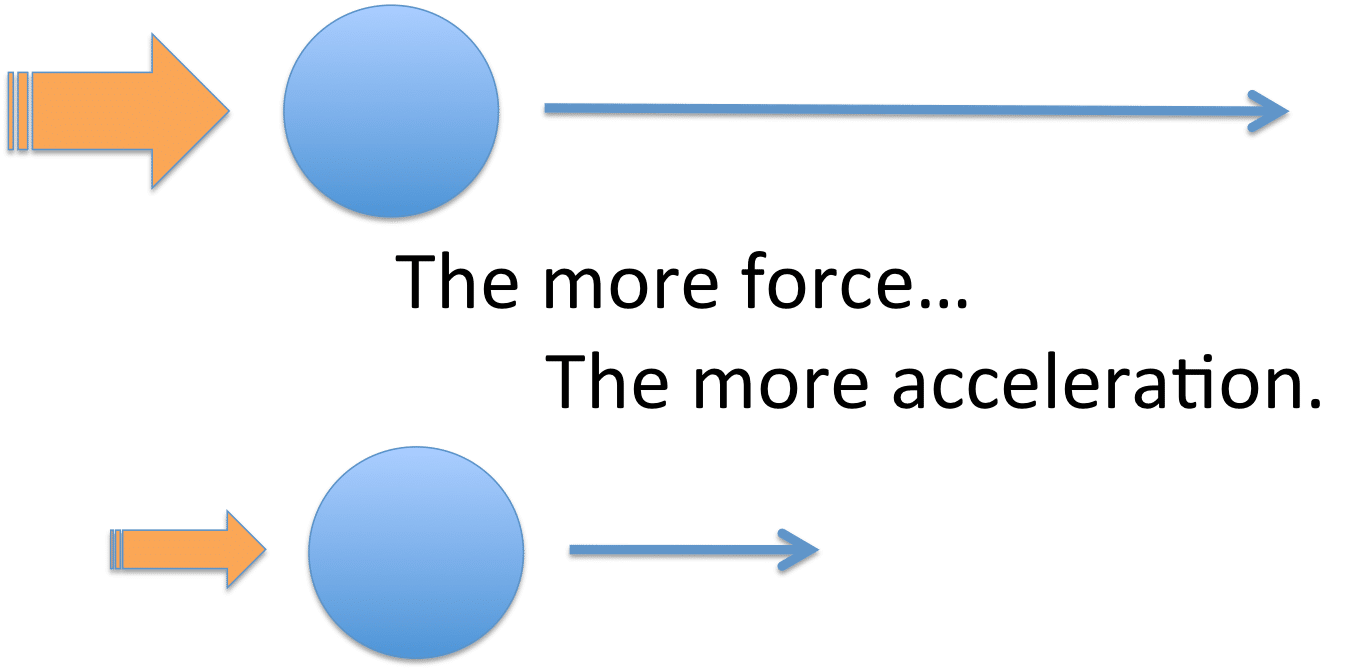
Web newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the. Web component form of newton’s second law. Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to the mass of that body times its rate of acceleration. Web this allows us to calculate, correspondingly, the x component and y component of the acceleration vector of our system. This vector equation can be written as three. Web (a) two students push a stalled car. This video reviews newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass. So, u n i t o f f o r c e = k × ( 1 k g) × ( 1 m s − 2) the second law of motion gives us a. Web a is the acceleration. Web newton’s second law of motion.
Web a is the acceleration. Web newton's second law of motion states the acceleration of an object is dependent on the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to the mass of that body times its rate of acceleration. Web we have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in (figure). This video reviews newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web si unit of force is newton (n). Web component form of newton’s second law. Web t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it.
Newton's Second Law CK12 Foundation
Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. This vector equation can be written as three component equations: Web si unit of force is newton (n). Web use the component form of newton's second law to write an expression for the y component of the net.
Newton's Second Law Of Motion
Web this allows us to calculate, correspondingly, the x component and y component of the acceleration vector of our system. This video reviews newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass. The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external.
Applications of Newton's Second Law of Motion (GA_MNLM18) YouTube
We have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in. This is called the equation for rotational. Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to the mass of that body times its rate of acceleration. Web a is the acceleration. Web newton’s.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Web newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the. Web use the component form of newton's second law to write an expression for the y component of the net force, fy. According to newton’s second law: This video reviews.
Newton’s Second Law
So, u n i t o f f o r c e = k × ( 1 k g) × ( 1 m s − 2) the second law of motion gives us a. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web (a) two students push a stalled car. Web use the component form of newton's second law to write an.
10 Examples of Newton’s Second Law of Motion in Everyday Life StudiousGuy
The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system. This vector equation can be written as three. So, u n i t o f f o r c e = k × ( 1 k g) × ( 1 m s − 2) the second law.
EduMission Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Newton's Second Law of Motion
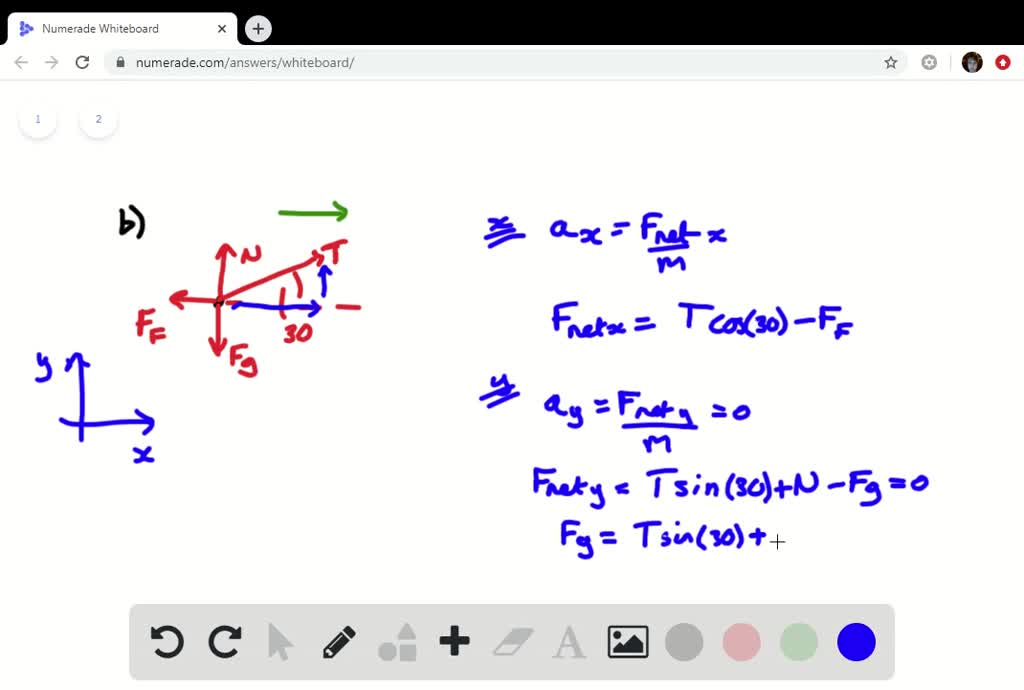
All external forces acting on the car are shown. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the. Web (a) two students push a stalled car. Web we have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in (figure). Web this allows us to calculate, correspondingly, the x component and y component of the acceleration.
PPT Chapter 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2918914
Express your answer in terms of some or all of the. Web newton’s second law of motion is more quantitative and is used extensively to calculate what happens in situations involving a force. Web newton’s second law of motion. So, u n i t o f f o r c e = k × ( 1 k g) × (.
SOLVED" Write Newton's second law in component form for each of the
This video reviews newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass. Web newton's second law of motion states the acceleration of an object is dependent on the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. All external forces acting on the car are shown. Web.
Newton’s second law
Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web component form of newton’s second law. All external forces acting on the car are shown. Web newton’s second law of motion is more quantitative and is used extensively to calculate what.
This Is Called The Equation For Rotational.
This video reviews newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass. The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system. This vector equation can be written as three. We have developed newton’s second law and presented it as a vector equation in.
Web Newton’s Second Law Of Motion.
Web component form of newton’s second law. Before we can write down. Web use the component form of newton's second law to write an expression for the y component of the net force, fy. Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to the mass of that body times its rate of acceleration.
Web Newton's Second Law Of Motion States The Acceleration Of An Object Is Dependent On The Net Force Acting On The Object And The Mass Of The Object.
All external forces acting on the car are shown. Web a is the acceleration. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the. Web in its basic form, newton's second law states that the sum of the forces on a body will be equal to mass of that body times the rate of acceleration.
This Vector Equation Can Be Written As Three Component Equations:
Web newton’s second law of motion. Web (a) two students push a stalled car. Web this allows us to calculate, correspondingly, the x component and y component of the acceleration vector of our system. Web t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it.


.PNG)
.PNG)