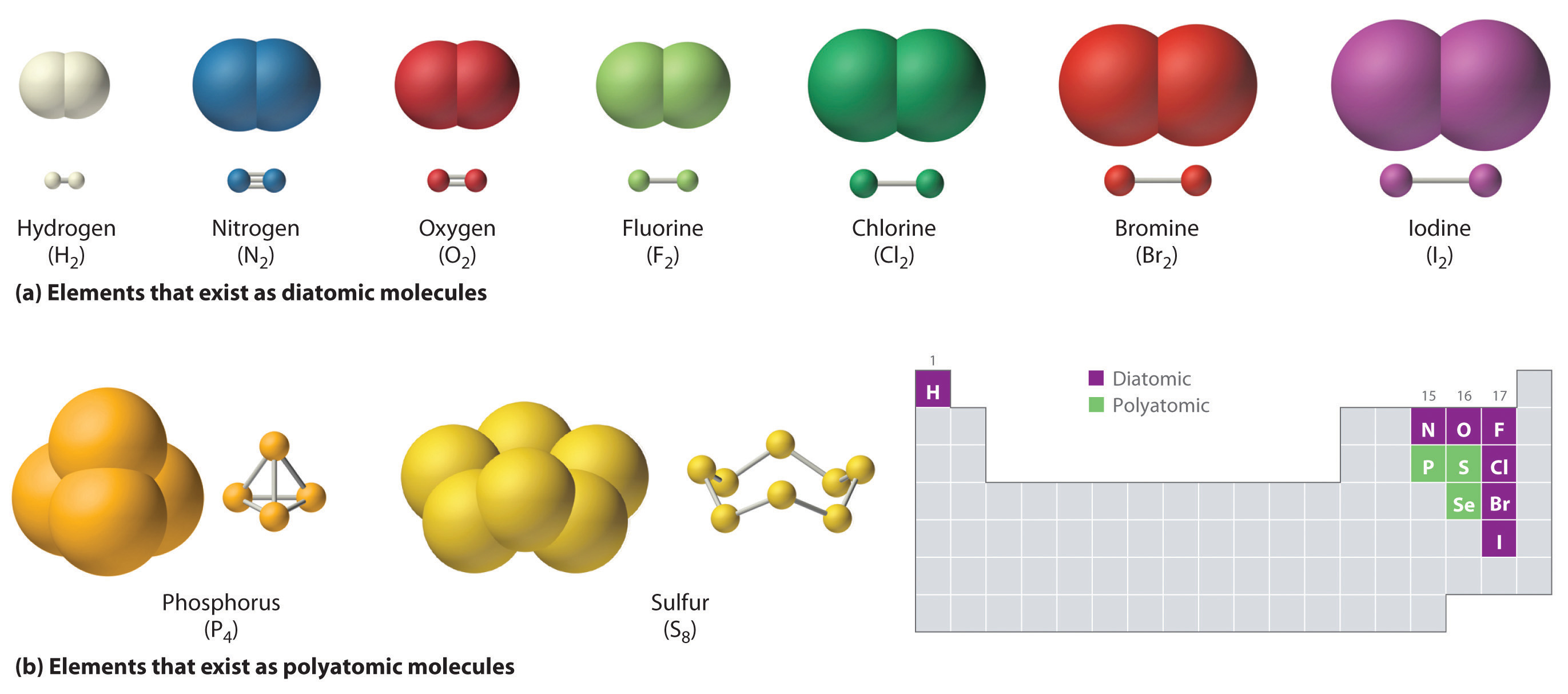
Atoms Of Which Two Elements Will Form An Ionic Bond
Atoms Of Which Two Elements Will Form An Ionic Bond - Let’s consider both types of. In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. An atom of sodium will lose an electron and form a positive ion. Web covalent and ionic bonds are both typically considered strong bonds. Web the formation of ionic compounds. Positive charges repel each other, so an ionic compound is not likely between two. These bonds form when an electron is shared between two elements and are the. One atom acts as an electron donor, and the other as an. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
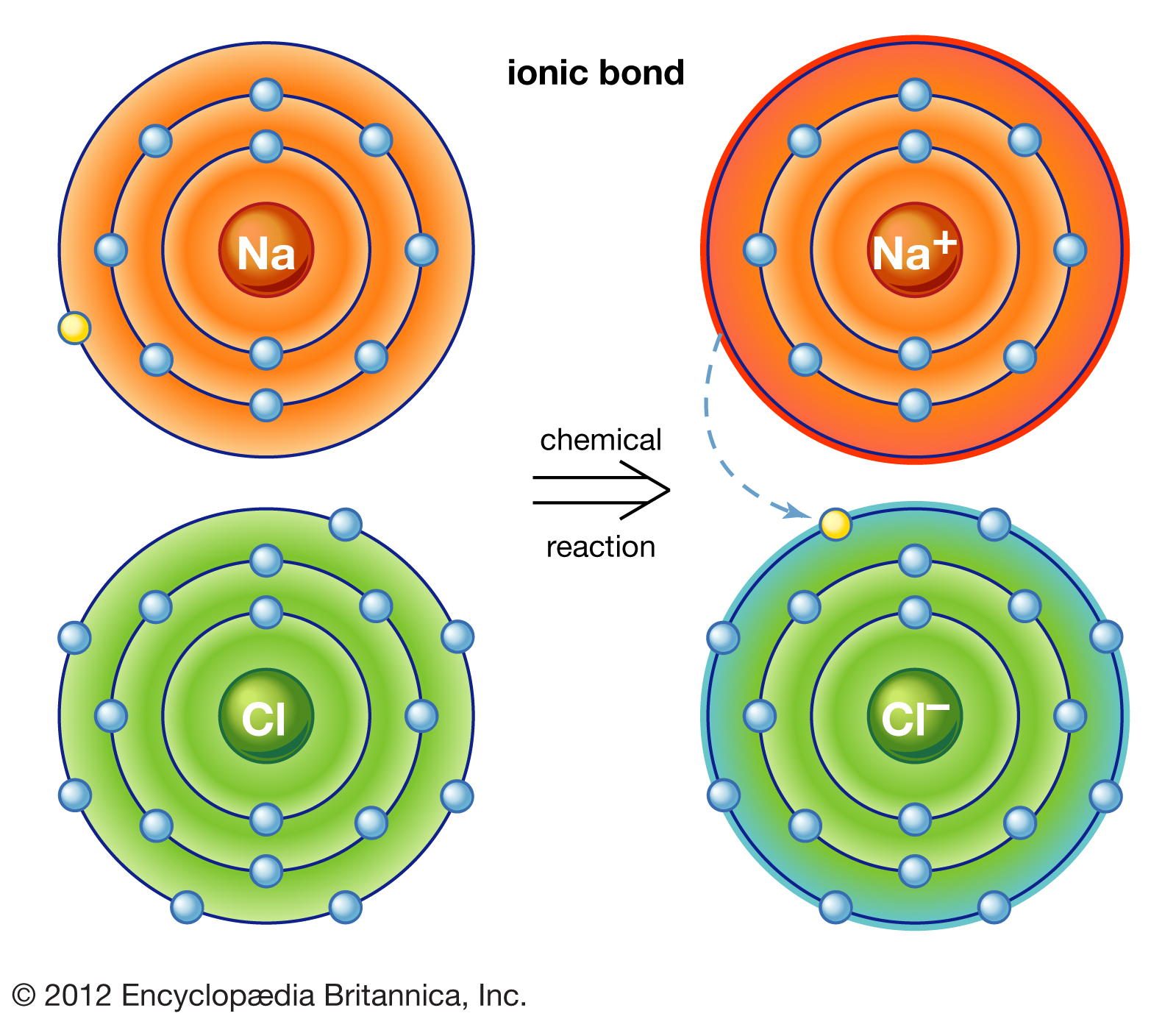
Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. These bonds form when an electron is shared between two elements and are the. Web the formation of ionic compounds. Web covalent and ionic bonds are both typically considered strong bonds. In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Finally, the column with n at the top and p just below. Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion.
In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Ionic bonds are formed by transfer of electrons between metal and non metals. Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion. Web covalent and ionic bonds are both typically considered strong bonds. Ionic bonds and covalent bonds. A metal (which forms the cations) and a nonmetal (which forms the anions). Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
Difference Between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds Definition
Web another type of strong chemical bond between two or more atoms is a covalent bond. Web the formation of ionic compounds. Web as we have seen, there are two types of bonds: Web covalent and ionic bonds are both typically considered strong bonds. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more.
How Does An Ionic Bond Form Between Sodium And Chlorine slideshare
Finally, the column with n at the top and p just below. Positive charges repel each other, so an ionic compound is not likely between two. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. Web in covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic bonds, electrons are fully transferred between two atoms so.
2.2 Chemical Bonds Anatomy & Physiology
Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Binary ionic compounds are composed of just two elements: In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together.
CH150 Chapter 3 Ions and Ionic Compounds Chemistry
Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Ionic bonds and covalent bonds. In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction. Positive charges repel each other, so an ionic compound is not likely between two.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction. Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Finally, the column with n at the top and p just below. Web ionic bonds form between two or.
Examples of Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Finally, the column with n at the top and p just below. Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Ionic bonds and covalent bonds. In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the electrostatic forces in the attraction.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Web another type of strong chemical bond between two or more atoms is a covalent bond. A metal (which forms the cations) and a nonmetal (which forms the anions). Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. This exchange results in a more.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
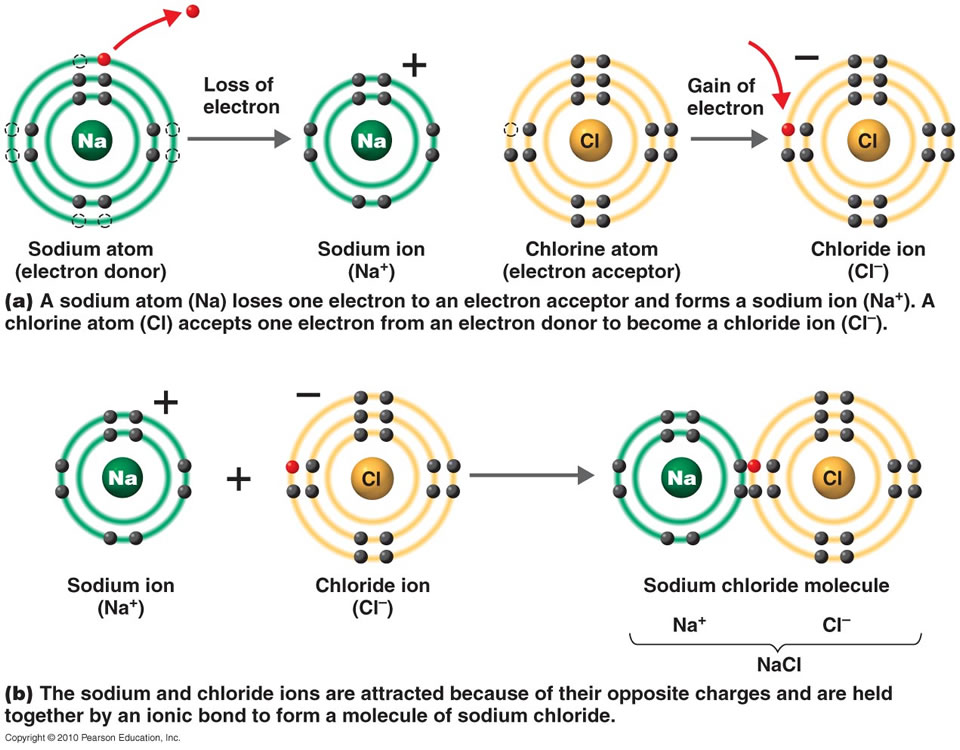
An atom of sodium will lose an electron and form a positive ion. These bonds form when an electron is shared between two elements and are the. Let’s consider both types of. However, other kinds of more temporary bonds can also form between atoms or molecules. Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond in which valence electrons are lost.
chemistry knowledge Comparison between Covalent and Ionic Bond
Web another type of strong chemical bond between two or more atoms is a covalent bond. Web the formation of ionic compounds. Positive charges repel each other, so an ionic compound is not likely between two. Web as we have seen, there are two types of bonds: Let’s consider both types of.
savvychemist Ionic Bonding (2) Dot and cross diagrams/Lewis structures
Gaining two electrons makes these atoms become a negative two charge in ionic bonding. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. One atom acts as an electron donor, and.
Ionic Bonding Is A Type Of Chemical Bond In Which Valence Electrons Are Lost From One Atom And Gained By Another.
However, other kinds of more temporary bonds can also form between atoms or molecules. Ionic bonds are formed by the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Binary ionic compounds are composed of just two elements: Let’s consider both types of.
Web In Covalent Bonds, Two Atoms Share Pairs Of Electrons, While In Ionic Bonds, Electrons Are Fully Transferred Between Two Atoms So That Ions Are Formed.
Web as we have seen, there are two types of bonds: Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion. A metal (which forms the cations) and a nonmetal (which forms the anions). Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms.
In An Ionic Bond, The Atoms Are Bound Together By The Electrostatic Forces In The Attraction.
Positive charges repel each other, so an ionic compound is not likely between two. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. This exchange results in a more stable, noble gas.
Gaining Two Electrons Makes These Atoms Become A Negative Two Charge In Ionic Bonding.
Web covalent and ionic bonds are both typically considered strong bonds. These bonds form when an electron is shared between two elements and are the. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
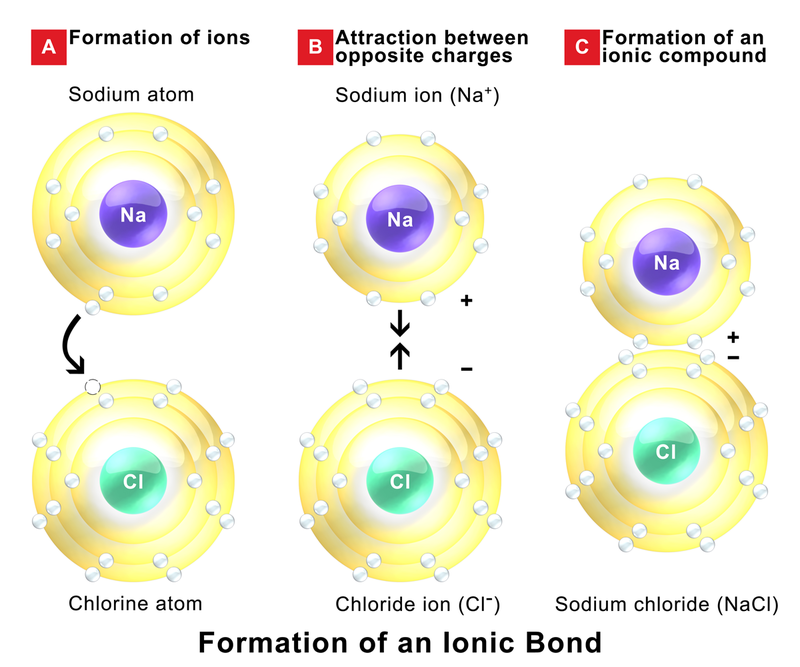
.PNG)



/ionic-bond-58fd4ea73df78ca1590682ad.jpg)