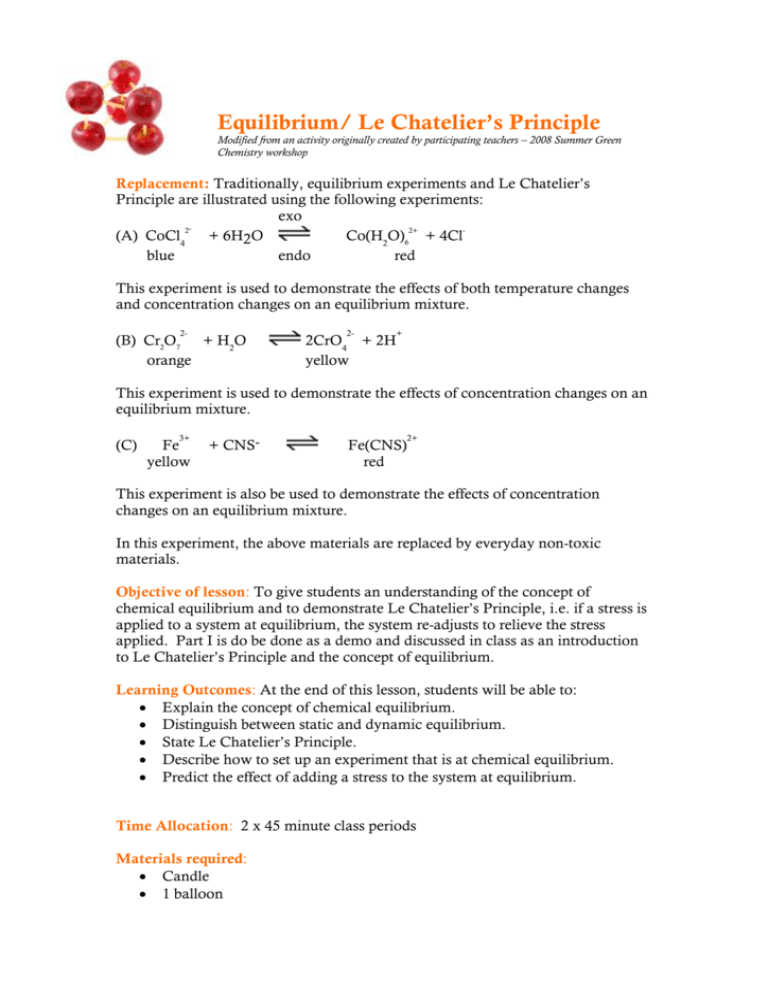
Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium Answer Key
Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium Answer Key - Web changing the volume and pressure of an equilibrium system shifts the equilibrium only if the number of moles and gaseous reactants is different from the number of moles of a gaseous products. One thing to note about equilibrium is that the reactions do not. No net change in the amount of reactants and products occurs in the chemical. H 2 (g) + cl 2 (g) 2hcl(g) k eq = [hcl]2 [h 2][cl 2] b. True or false, chemical equilibrium is a state in which the forward and reverse reactions take place. Web chapter 18 chemical equilibrium. Web terms in this set (16) what happens in reversible actions. 3a( aq ) + b( aq ) 2c( aq ) + 3d( aq ) ← a. At 793 k, the equilibrium. When the rate of a reactions forward reaction equals the rate of its reverse reaction and the concentrations of its products and reactants remain unchanged.
When the rate of a reactions forward reaction equals the rate of its reverse reaction and the concentrations of its products and reactants remain unchanged. One thing to note about equilibrium is that the reactions do not. Web terms in this set (16) what happens in reversible actions. Web the equation for k (the equilibrium constant); * pdf chemistry 101 answer key 1 review questions chapter 7 chemistry 101. Alcohols and esters, atomic structure and theory, benzene, chemical compound, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, acyl compounds, chemical. Web download chapter 18 chemical equilibrium test answer key: Web terms in this set (8) reversible reaction. Web the chapter carbonyl compounds mcqs covers topics of carbonyl compounds, aldehydes and ketone testing, nucleophilic addition with hcn, preparation of aldehydes and ketone, reduction of aldehydes, and ketone. Web the presence of three strong bonds makes n 2 a very stable molecule.
Fundamentals of analytical chemistry princeton review chapter 1. N 2 (g) + 3 h 2 (g) 2 nh 3 (g) k eq 3= [nh ]2. Nh4hs(g) nh3(g) + h2s(g) b. Web the presence of three strong bonds makes n 2 a very stable molecule. Chapter 18 chemical equilibrium test answer key | updated. When the rate of a reactions forward reaction equals the rate of its reverse reaction and the concentrations of its products and reactants remain unchanged. Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10. Web the equation for k (the equilibrium constant); Click the card to flip 👆. Cuso.3h20(s) + 2h20(g) cus04.5hoo(s) 2.
8+ Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium Answer Key SarbjitDariya
N 2 (g) + 3 h 2 (g) 2 nh 3 (g) k eq 3= [nh ]2. 2h 2 + o 2 ⇄ 2h 2 o. One thing to note about equilibrium is that the reactions do not. Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10. Write the equilibrium expression for the following hypothetical equation:
Writing An Equilibrium Expression Chem Worksheet 18 2 Answers
How do you find free textbook answer keys? Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10. Web terms in this set (16) what happens in reversible actions. Write equilibrium expressions for the following reactions. Cuso.3h20(s) + 2h20(g) cus04.5hoo(s) 2.
Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium
Web the equation for k (the equilibrium constant); Alcohols and esters, atomic structure and theory, benzene, chemical compound, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, acyl compounds, chemical. Fundamentals of analytical chemistry princeton review chapter 1. * pdf chemistry 101 answer key 1 review questions chapter 7 chemistry 101. Web answer answer the following questions in the space provided.
CHAPTER 17 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
4hcl@) + 02(g) 2c12(g) + 2h20(g) c. 3a( aq ) + b( aq ) 2c( aq ) + 3d( aq ) ← a. No net change in the amount of reactants and products occurs in the chemical. * pdf chemistry 101 answer key 1 review questions chapter 7 chemistry 101. Web 18 chemical equilibrium 1.
Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium
Web changing the volume and pressure of an equilibrium system shifts the equilibrium only if the number of moles and gaseous reactants is different from the number of moles of a gaseous products. H 2 (g) + cl 2 (g) 2hcl(g) k eq = [hcl]2 [h 2][cl 2] b. Web terms in this set (8) reversible reaction. How do you.
10 Best Images of Unit Rate Word Problems Worksheet Rates Worksheets
3a( aq ) + b( aq ) 2c( aq ) + 3d( aq ) ← a. Energy is emitted by this transition. Web the equation for k (the equilibrium constant); Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for each of the following reactions. At 793 k, the equilibrium.
8+ Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium Answer Key SarbjitDariya
Web questions and answers (mcqs) is a revision guide with a collection of trivia quiz questions and answers on topics: How do you find free textbook answer keys? Web 18 chemical equilibrium 1. 4hcl@) + 02(g) 2c12(g) + 2h20(g) c. Energy is emitted by this transition.
PPT Chemical Equilibrium Chapter 18 Modern Chemistry PowerPoint
No net change in the amount of reactants and products occurs in the chemical. Write equilibrium expressions for the following reactions. H 2 (g) + cl 2 (g) 2hcl(g) k eq = [hcl]2 [h 2][cl 2] b. Therefore, it must fulfill its bonding requirement by forming. Pc15(g) pc13(g) + c12(g) d.
Chapter 17 Chemical Equilibrium
Web write the equilibrium equation between elemental hydrogen and elemental oxygen as reactants and water as the product. Fundamentals of analytical chemistry princeton review chapter 1. Energy is emitted by this transition. Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10. 3a( aq ) + b( aq ) 2c( aq ) + 3d( aq ) ← a.
KEY Equilibrium Practice 4
Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10. Web terms in this set (8) reversible reaction. Web chemical equilibrium 18 3 answer key. Web one in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously. Write equilibrium expressions for the following reactions.
Write Equilibrium Expressions For The Following Reactions.
Energy is emitted by this transition. Web the equation for k (the equilibrium constant); Web download chapter 18 chemical equilibrium test answer key: Calculate the molar solubility of agbr (ksp= 5.0x10.
Web Embark On A Journey Through Equilibrium Dynamics With The Chapter 18 Chemical Equilibrium Answer Key.
Some of the worksheets for this concept are chem 1 chemical equilibrium work answer keys, calculating equilibrium constants work 183 answer key, chemical equilibrium work answers, answer key 18. No net change in the amount of reactants and products occurs in the chemical. Web terms in this set (16) what happens in reversible actions. Web write the equilibrium equation between elemental hydrogen and elemental oxygen as reactants and water as the product.
4Hcl@) + 02(G) 2C12(G) + 2H20(G) C.
Cuso.3h20(s) + 2h20(g) cus04.5hoo(s) 2. 2h 2 + o 2 ⇄ 2h 2 o. Chapter 18 chemical equilibrium test answer key | full. Web the presence of three strong bonds makes n 2 a very stable molecule.
Write The Expression For The Equilibrium Constant For Each Of The Following Reactions.
H 2 (g) + cl 2 (g) 2hcl(g) k eq = [hcl]2 [h 2][cl 2] b. A state of balance in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal; One thing to note about equilibrium is that the reactions do not. Alcohols and esters, atomic structure and theory, benzene, chemical compound, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, acyl compounds, chemical.