Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation - Fermentation, anaerobic respiration, and aerobic respiration all produce atp using glycolysis to oxidize glucose to pyruvate with a net production of 2 atp by substrate level phosphorylation. One process cells used to get the energy they need to perform work is known as cell respiration. Adenosine triphosphate (atp) click the card to flip 👆. Life is work living cells require energy from outside sources some animals, such as the. Web chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation lectures by erin barley kathleen fitzpatrick overview: Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration and fermentation figure 9.1.a green parrot eating fruit. In the mitochondria, the nadh and the fadh₂ will be converted into atp. Web how does fermentation differ from cellular respiration? 2nd step in cellular respiration.
Web cellular respiration and fermentation figure 9.1.a green parrot eating fruit. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen, while cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes, but is often used to refer to the aerobic process, in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant. Adenosine triphosphate (atp) click the card to flip 👆. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without o2. Energy in living organisms 9.2. Web life is work living cells need energy to perform their tasks, such as creating polymers (figure 9.1). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and. Pyruvate oxidation / citric acid cycle 3. Cellular respiration, like burning, results in the complete oxidation of glucose into co2 and water. A preview there are three (3) metabolic stages to harvest energy from glucose:
2nd step in cellular respiration. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to generate atp ( both plants and animals use cellular respiration to make energy. Instead, small, reduced organic molecules are produced as waste. Web chapter 9, cellular respiration and fermentation. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… All living organisms break down food, especially carbohydrates, to obtain energy to do the work of being alive. Pyruvate oxidation / citric acid cycle 3. One process cells used to get the energy they need to perform work is known as cell respiration. Web a) anabolic pathways b) catabolic pathways c) fermentation pathways d) thermodynamic pathways e) bioenergetic pathways b the molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or.
PPT Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation PowerPoint
Life is work living cells require energy from outside sources some animals, such as the. Web the stages of cellular respiration: Links to chapter sections 9.1. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the immediate energy source that drives atp synthesis by atp synthase.
Cellular Respiration & Fermentation cell
2nd step in cellular respiration. Life is work living cells require energy from outside sources some animals, such as the. The ultimate energy for life comes from the sun. Web start studying chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration Fermentation (Chapter 9 part 5 of 5) YouTube
Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen, while cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes, but is often used to refer to the aerobic process, in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant. In the mitochondria, the nadh and the fadh₂ will be converted into atp. Energy in.
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Review YouTube
Cellular respiration, like burning, results in the complete oxidation of glucose into co2 and water. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like steps of cellular respiration:, glycolysis:, pyruvate processing: All living organisms break down food, especially carbohydrates, to obtain energy to do the work.
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
Web a) anabolic pathways b) catabolic pathways c) fermentation pathways d) thermodynamic pathways e) bioenergetic pathways b the molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen, while cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes, but is.
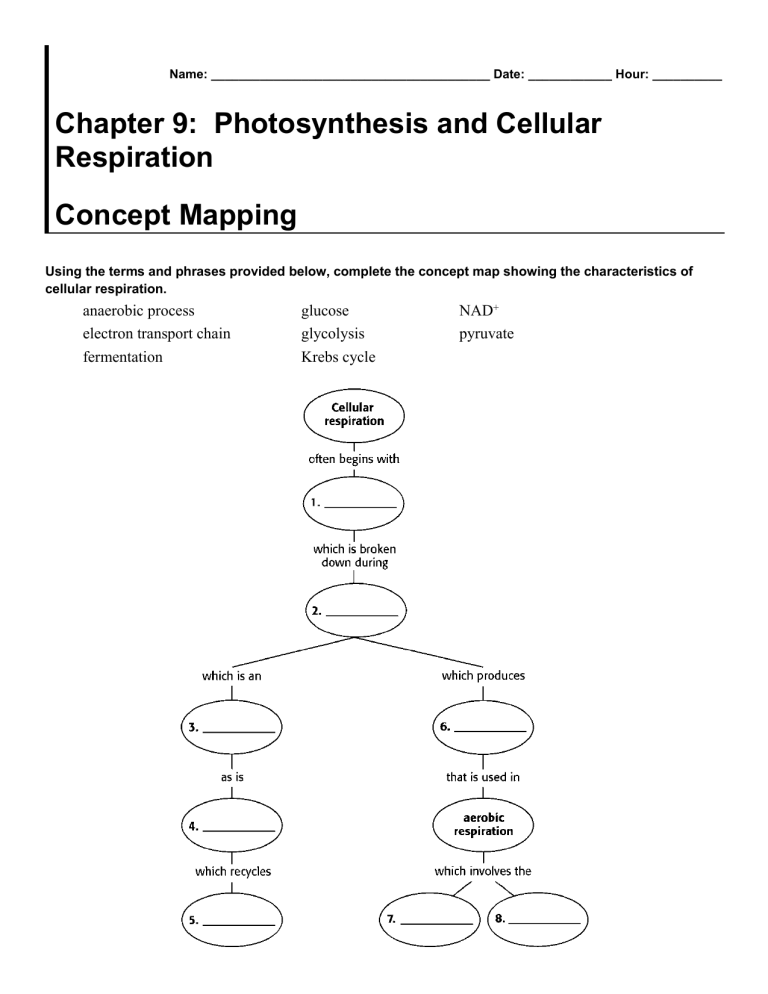
Chapter 9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Concept Mapping
Energy in living organisms 9.2. Fermentation, on the other hand, does not fully oxidize glucose. Web cellular respiration and fermentation figure 9.1.a green parrot eating fruit. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… Web how does fermentation differ from cellular respiration?
Chapter 9 (Cellular Respiration and Fermentation) Vocabulary
Overview of cellular respiration 9.3. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… Web start studying chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation. Web the stages of cellular respiration: Adenosine triphosphate (atp) click the card to flip 👆.
Get Who Does Cellular Respiration The Latest Mito
A molecule consisting of adenine, a sugar, and three phosphate groups that can be hydrolyzed to release energy. As a result, cellular respiration Energy in living organisms 9.2. Fermentation, anaerobic respiration, and aerobic respiration all produce atp using glycolysis to oxidize glucose to pyruvate with a net production of 2 atp by substrate level phosphorylation. The ultimate energy for life.
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation Study Guide Answers
Instead, small, reduced organic molecules are produced as waste. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and exists as heat (figure 9… Web life is work living cells need energy to perform their tasks, such as creating polymers (figure 9.1). 2nd step in cellular respiration.
PPT Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation PowerPoint
Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen, while cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes, but is often used to refer to the aerobic process, in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Links to chapter sections 9.1. All.
Cellular Respiration Is The Complete Breakdown Of Sugars Or Organic Molecules With O2 Being The Reactant.
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the immediate energy source that drives atp synthesis by atp synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the:, which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose. Fermentation, anaerobic respiration, and aerobic respiration all produce atp using glycolysis to oxidize glucose to pyruvate with a net production of 2 atp by substrate level phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration and fermentation figure 9.1.a green parrot eating fruit. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to generate atp ( both plants and animals use cellular respiration to make energy.
Web Explain The Difference Between Fermentation And Cellular Respiration.
Web how does fermentation differ from cellular respiration? Web the stages of cellular respiration: Energy in living organisms 9.2. Cellular respiration, like burning, results in the complete oxidation of glucose into co2 and water.
Web A) Anabolic Pathways B) Catabolic Pathways C) Fermentation Pathways D) Thermodynamic Pathways E) Bioenergetic Pathways B The Molecule That Functions As The Reducing Agent (Electron Donor) In A Redox Or.
The reaction releases energy to the surroundings because the electrons lose. Life is work living cells require energy from outside sources some animals, such as the. Web a metabolic process that breaks down carbohydrates and sugars through a series of reactions to either pyruvic acid or lactic acid and release energy for the body in the form of atp. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and.
Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp) Click The Card To Flip 👆.
Web chapter 9, cellular respiration and fermentation. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like steps of cellular respiration:, glycolysis:, pyruvate processing: Web life is work living cells need energy to perform their tasks, such as creating polymers (figure 9.1). Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen, while cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes, but is often used to refer to the aerobic process, in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant.