Cooperate To Form The Placenta
Cooperate To Form The Placenta - How does the placenta form? Web the placenta is a fetal organ made up of its parenchyma, chorion, amnion, and umbilical cord. It’s made up of blood vessels and provides your developing baby with. Whether you’re looking for a way to gather. Web the placenta, an organ that develops inside your uterus, provides a connection between you and your baby. (and at this point the uterus stops secreting glycogen.) here's how it works: Currently, after fecundation and successive cell divisions, the. Web at about 8 to 12 weeks into pregnancy, the placenta takes over as a nutrient source for your baby. Web the placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus during pregnancy. The placenta can form anywhere in your uterus.
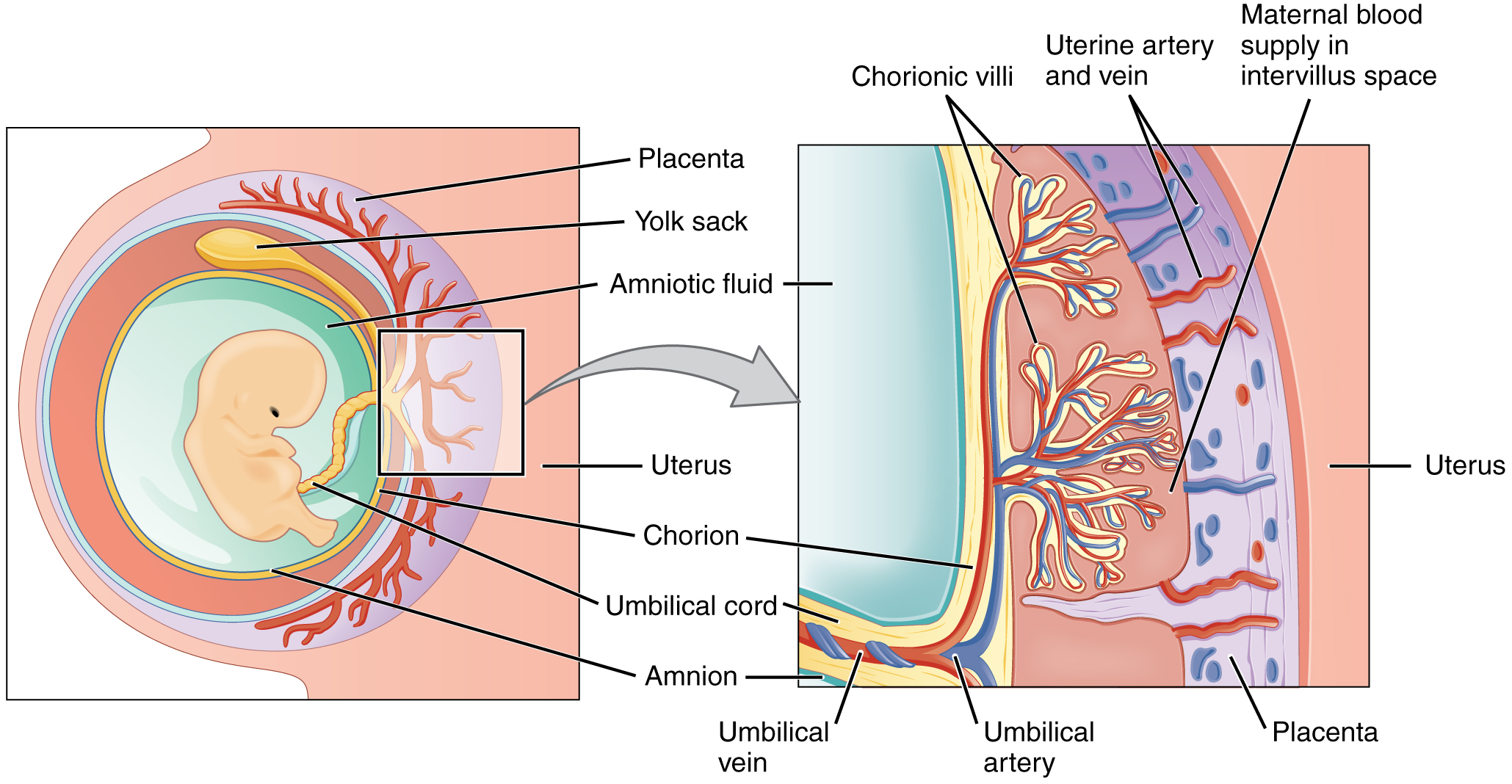
This connection (via the umbilical cord) is what helps to sustain your. This timeline compares development of the fetus and the placenta across 40 weeks of pregnancy. Web at about 8 to 12 weeks into pregnancy, the placenta takes over as a nutrient source for your baby. People have also been known. Via the umbilical cord and the chorionic villi, this organ delivers. These tissues are used to create medical products, including wound coverings for. It’s made up of blood vessels and provides your developing baby with. Web the placenta is a fetal organ made up of its parenchyma, chorion, amnion, and umbilical cord. Whether you’re looking for a way to gather. Web feb 12, 2021 nicole levine illustration:
Web the most common placenta preparation — creating a capsule — is made by steaming and dehydrating the placenta or processing the raw placenta. The polar body doesn't have a cytoplasm &&. Whether you’re looking for a way to gather. Web a consent form is a signed document that outlines the informed consent of an individual for a medical study, clinical trial, or activity. Web our placenta donor program allows mothers to donate postnatal tissue after their baby is born. The timeline of placental development illustrates. Via the umbilical cord and the chorionic villi, this organ delivers. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta so that nutrients,. Currently, after fecundation and successive cell divisions, the. The placenta plays an absolutely crucial and essential role during the nine months of pregnancy.
Placental immune editing switches (PIES) and cancer progression
Other cells develop into an inner layer of membranes. Web the placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus during pregnancy. Web the most common placenta preparation — creating a capsule — is made by steaming and dehydrating the placenta or processing the raw placenta. By donating your placenta and umbilical cord, you give. Web some of the cells from.
When does the placenta form, and what does it do? Learn all about the
Whether you’re looking for a way to gather. Web some of the cells from the placenta develop into an outer layer of membranes (chorion) around the developing blastocyst. Web a consent form is a signed document that outlines the informed consent of an individual for a medical study, clinical trial, or activity. Web the placenta is an organ that develops.
The Placenta Answers in Genesis
Web a consent form is a signed document that outlines the informed consent of an individual for a medical study, clinical trial, or activity. Web where does the placenta form? The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta so that nutrients,. Web the placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus during pregnancy. Web in humans, the placenta usually.
Placenta Definition, Anatomy and Functions
Web the most common placenta preparation — creating a capsule — is made by steaming and dehydrating the placenta or processing the raw placenta. Web in humans, the placenta usually has a disc shape, but size varies vastly between different mammalian species. People have also been known. This timeline compares development of the fetus and the placenta across 40 weeks.
Basic structure of the placenta showing maternal and fetal sides and
Web the placenta is a structure that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. In most pregnancies, the placenta is located at the top or side of the uterus. Other cells develop into an inner layer of membranes. Web the most common placenta preparation — creating a capsule — is made by steaming and dehydrating the placenta or processing the raw.
Understanding the Placenta YouTube
The timeline of placental development illustrates. Web after the blastocyst which will develop into the fetus makes contact with the uterine wall, blastocyst and maternal tissue grow together to form a single, cooperating organ that. Whether you’re looking for a way to gather. Web the placenta is a structure that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. Web our placenta donor.
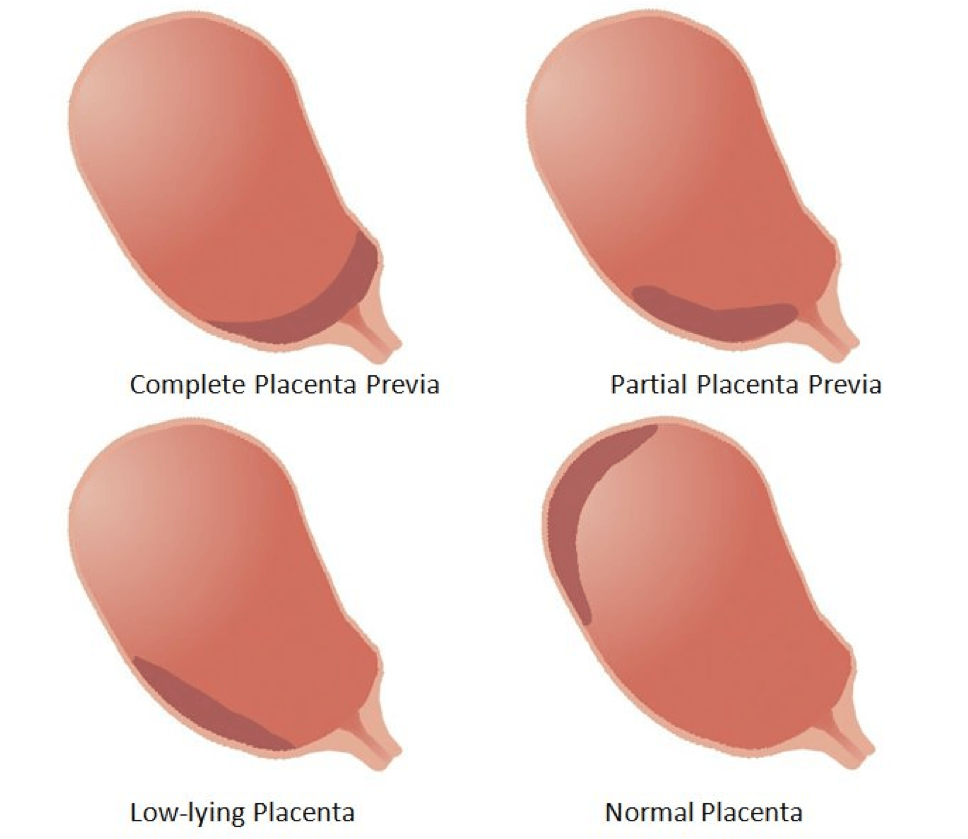
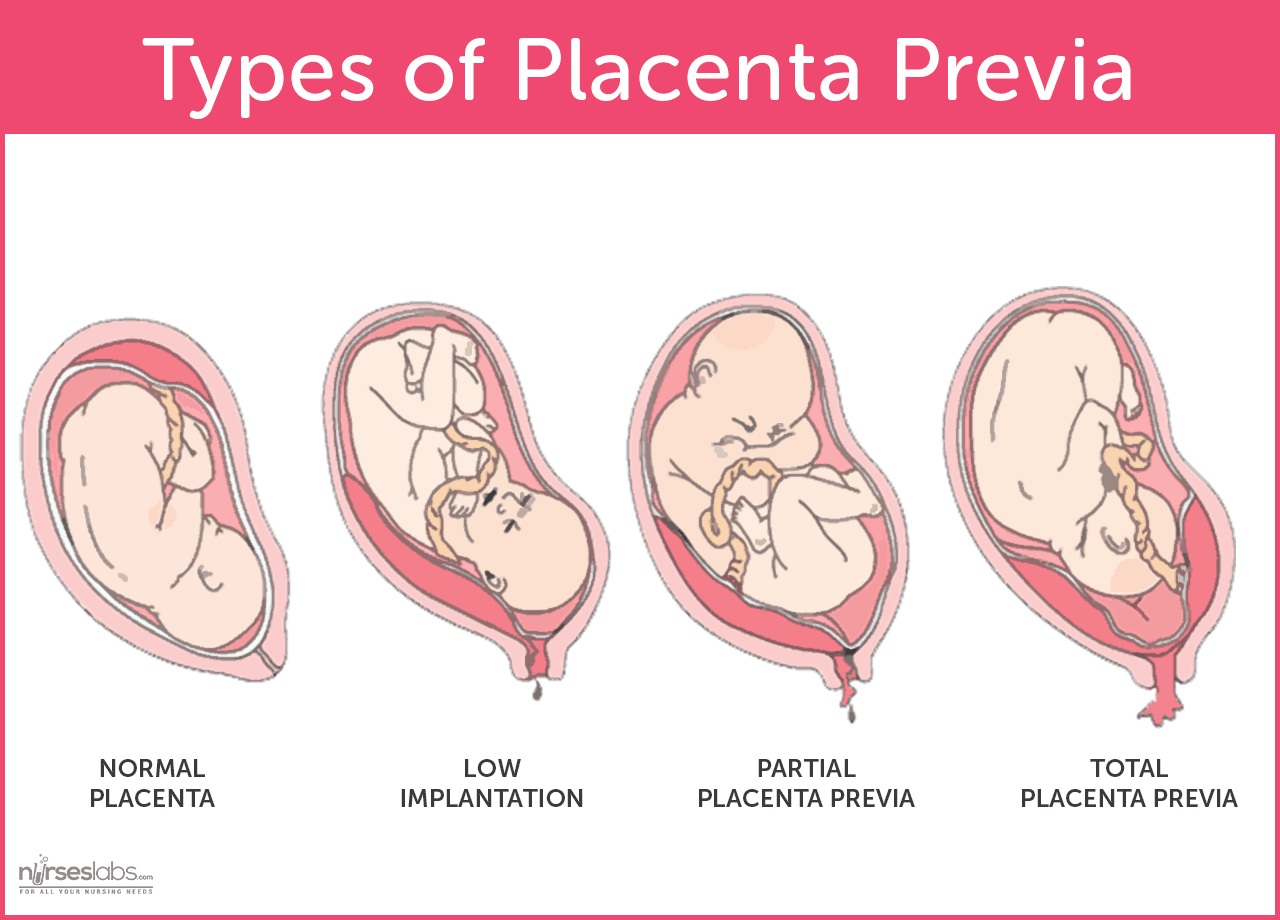
Placenta Placenta praevia Ontario Fetal Centre
The following illustrations show how the human placenta develops. In most pregnancies, the placenta is located at the top or side of the uterus. Currently, after fecundation and successive cell divisions, the. Web the placenta, an organ that develops inside your uterus, provides a connection between you and your baby. The placenta determines how fetuses eat, breathe.
The Push to Understand the Placenta The New York Times
(and at this point the uterus stops secreting glycogen.) here's how it works: Web the placenta is an organ that develops during pregnancy in a gradual and poorly understood process. Web the placenta is a structure that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. Web the placenta, an organ that develops inside your uterus, provides a connection between you and your.
Placenta Previa Nursing Care Plan and Management
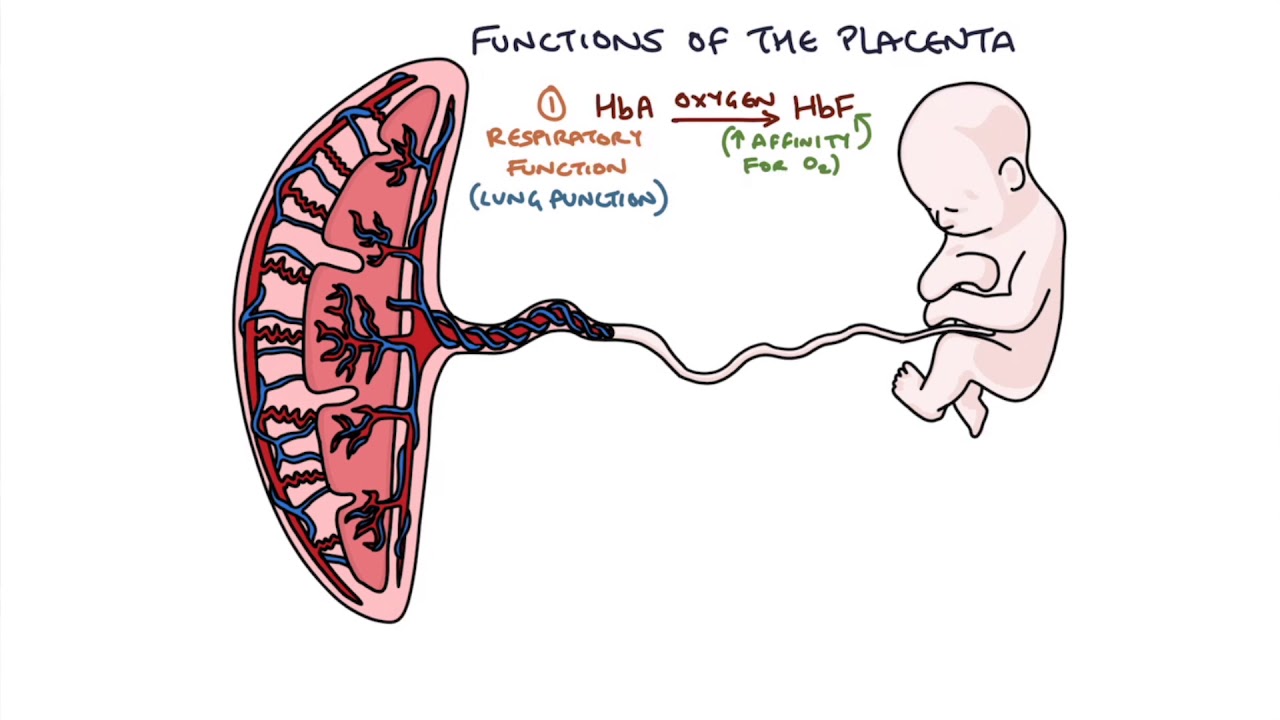
More specifically, it provides nutrition and oxygen to the fetus and removes waste. The placenta determines how fetuses eat, breathe. The placenta plays an absolutely crucial and essential role during the nine months of pregnancy. Web the most common placenta preparation — creating a capsule — is made by steaming and dehydrating the placenta or processing the raw placenta. Between.
Development of the placenta By OpenStax (Page 5/57) Jobilize
It’s made up of blood vessels and provides your developing baby with. The timeline of placental development illustrates. (and at this point the uterus stops secreting glycogen.) here's how it works: Web the placenta is a structure that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. Web the main function of the placenta is the interchange between the mother and the fetus.
Web Birth Tissue Donation Moms Who Give Birth Via Cesarean Section Have The Option To Donate Their Birth Tissue To Connectlife.
Web some of the cells from the placenta develop into an outer layer of membranes (chorion) around the developing blastocyst. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta so that nutrients,. The placenta plays an absolutely crucial and essential role during the nine months of pregnancy. Web the placenta is a fetal organ made up of its parenchyma, chorion, amnion, and umbilical cord.
In Most Pregnancies, The Placenta Is Located At The Top Or Side Of The Uterus.
(and at this point the uterus stops secreting glycogen.) here's how it works: The placenta occasionally takes a form in which it comprises. Web in humans, the placenta usually has a disc shape, but size varies vastly between different mammalian species. The fetal structures form from the zygote and therefore separate the fetus from the.
The Placenta Determines How Fetuses Eat, Breathe.
This connection (via the umbilical cord) is what helps to sustain your. How does the placenta form? Web where does the placenta form? Other cells develop into an inner layer of membranes.
The Placenta Can Form Anywhere In Your Uterus.
Currently, after fecundation and successive cell divisions, the. The following illustrations show how the human placenta develops. It provides vital nutrients and oxygen to your baby through the umbilical cord. It develops wherever the fertilized egg implants into your uterine wall.