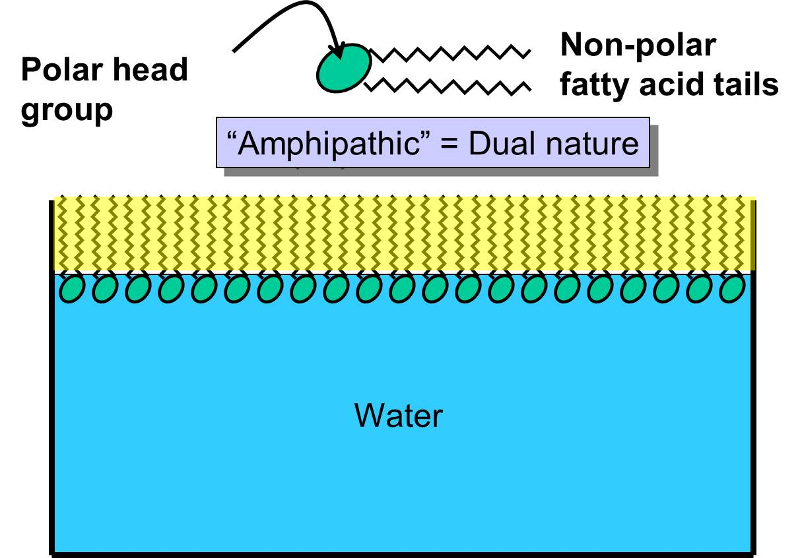
Explain Why Phospholipids Spontaneously Form Bilayer When Mixed With Water
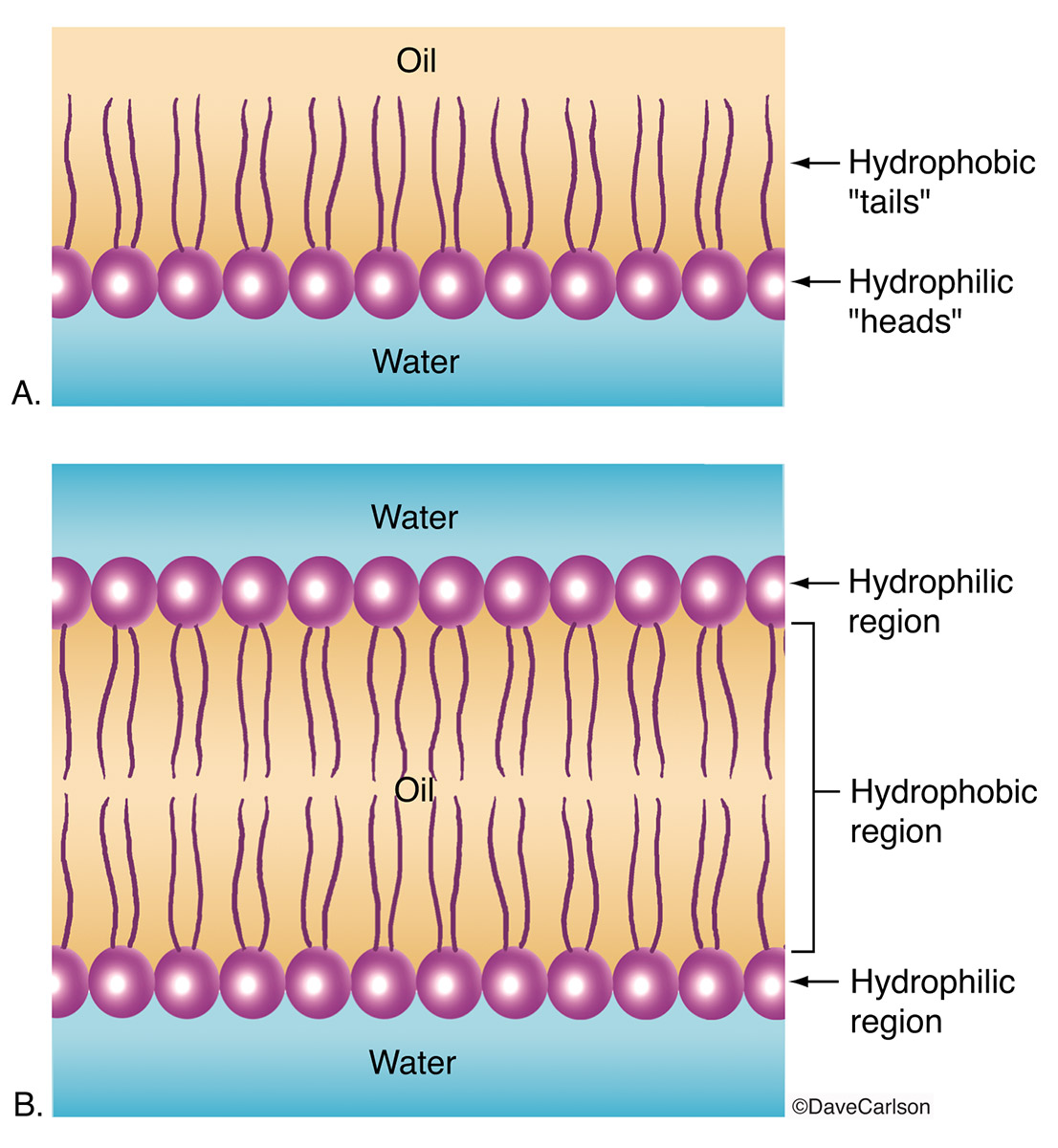
Explain Why Phospholipids Spontaneously Form Bilayer When Mixed With Water - Why do the heads of the phospholipids point. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Web the heads are attracted to the water. A) because of their conical shape and the attraction of the tails to each other b) because of. Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to. Web phospholipids a molecule that is a part of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head (phosphate group) and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.(2. Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to aggregate with. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water (2 points)? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water?
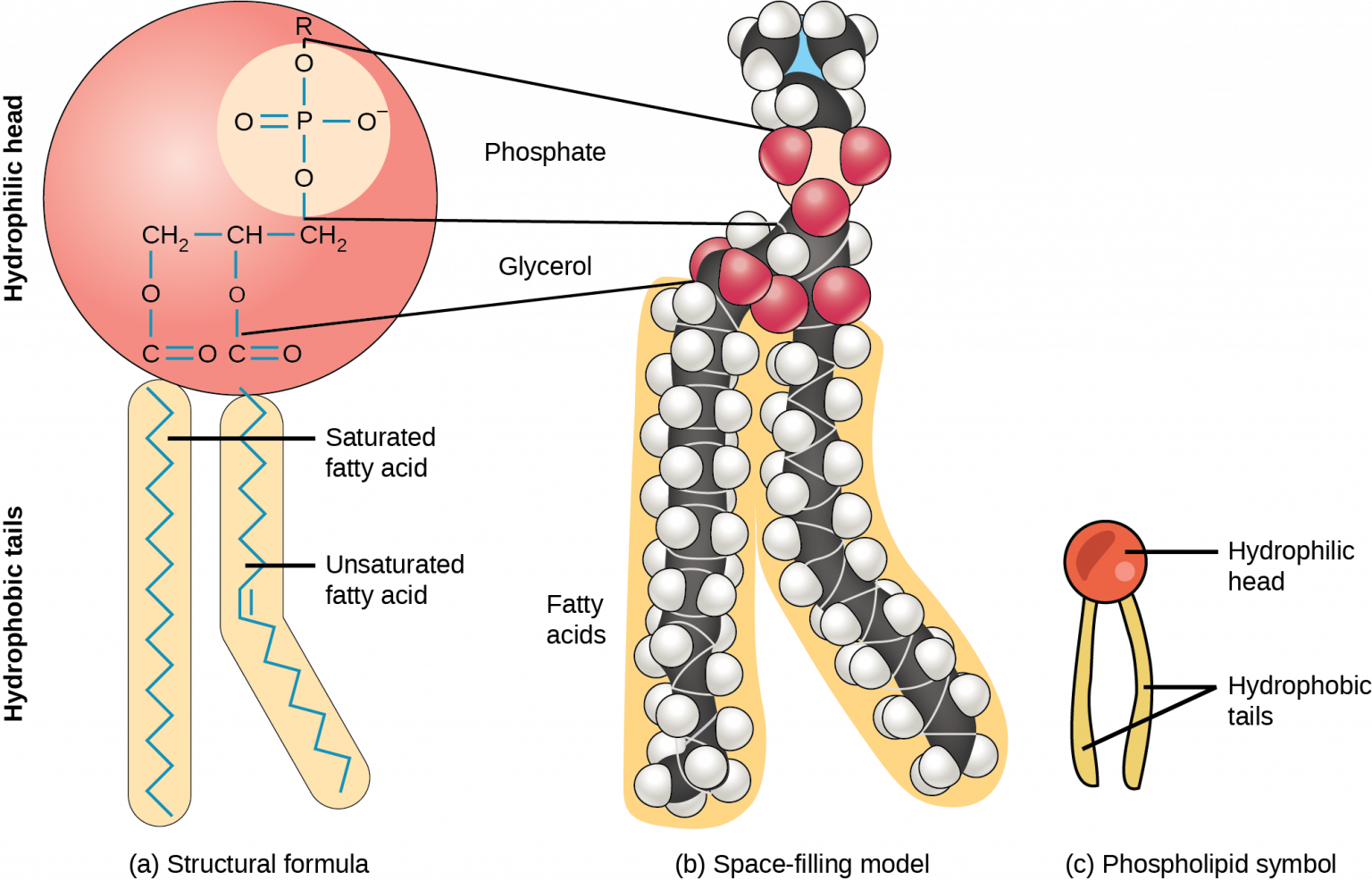
Web as phospholipids continue to saturate water, they spontaneously form into a bilayer. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Why do the heads of the phospholipids point. Web because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in. The polar hydrophilic head group. Because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane;. Ad high quality phosphatidic acid and dspe lipids available for research. Web solution verified by toppr in phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water.
Because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane; Phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water because they have an end that is. Web solution verified by toppr in phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water. A) because of their conical shape and the attraction of the tails to each other b) because of. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Various lipids available for phospholipid and lipid nanoparticle research. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer in an aqueous solution.
Solved Explain why phospholipids form bilayers in aqueous
Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in. Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a.
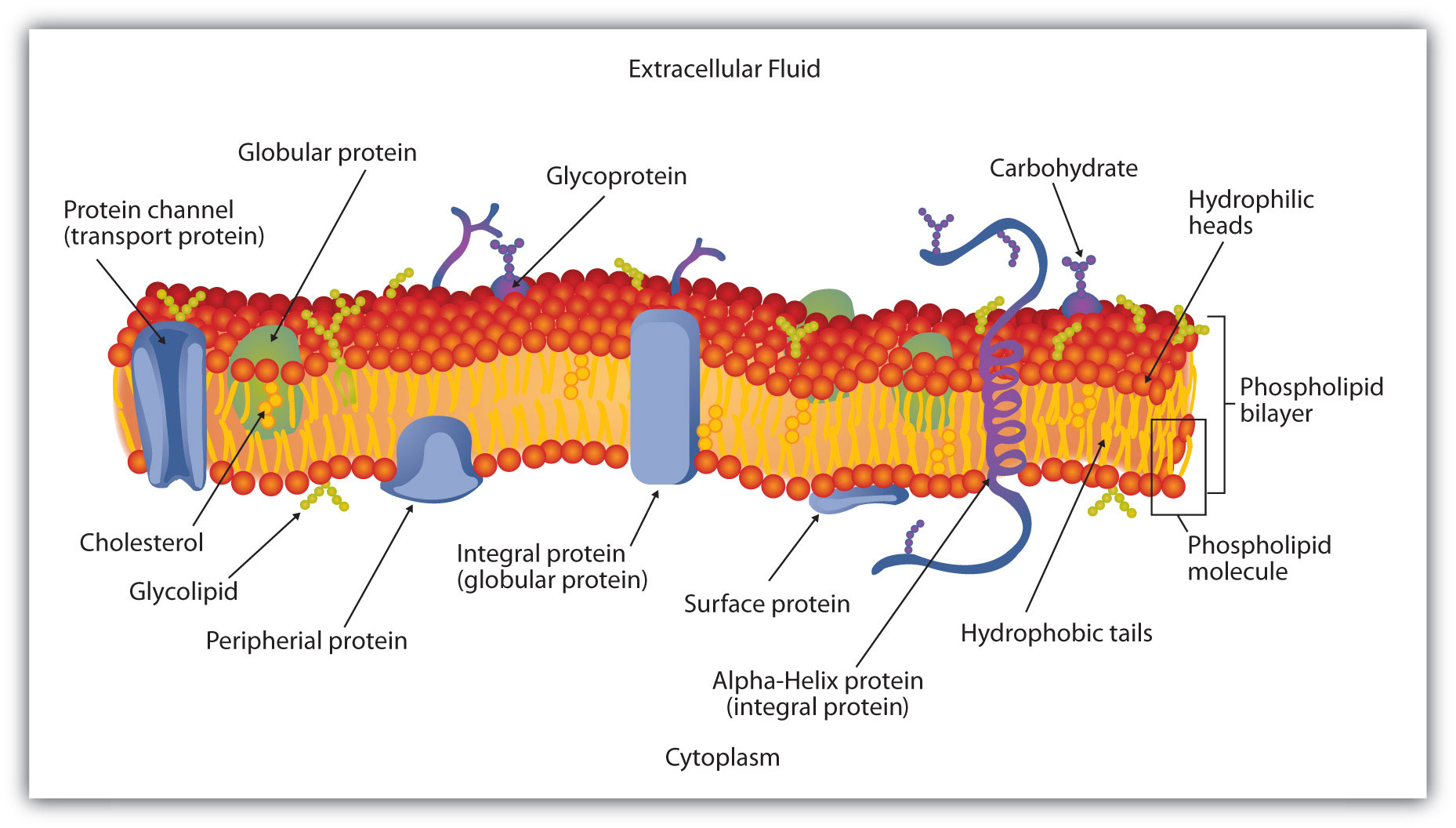
5.1B Fluid Mosaic Model Biology LibreTexts
The polar hydrophilic head group. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Two adjacent polar layers will directly contact water molecules creating a. Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane;
26.9 Phospholipids Chemistry LibreTexts
A and c b and c. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane; Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Web the heads are attracted to the water.
Lipids Microbiology
Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to. Why do the heads of the phospholipids point. Phospholipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other what property of the. A.
Phospholipid Layer & Bilayer Carlson Stock Art
Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Two adjacent polar layers will directly contact water molecules creating a. Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? A and c b and c. Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to.
Solved Com Iz Saved Help Consider Your Knowledge About Th...
Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? A and c b and c. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? But the phosphate group is hydrophilic, or soluble in water.
Chapter 3 Chemistry of Life Human Biology
The polar hydrophilic head group. Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? A) because of their conical shape and the attraction of the tails to each other b) because of. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web the heads are attracted to the water.
Membranes and Membrane Lipids
Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Two adjacent polar layers will directly contact water molecules creating a. Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? Phospholipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other what property of the. Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water?
LabXchange
Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Ad high quality phosphatidic acid and dspe lipids.
Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water slidesharetrick
Because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane; O because the polar head groups come together o because they. Various lipids available for phospholipid and lipid nanoparticle research. Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to aggregate with..
Web Solution Verified By Toppr In Phospholipids, The Two Fatty Acids Are Hydrophobic, Or Insoluble In Water.
The polar hydrophilic head group. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Question 3 (1 point) explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Two adjacent polar layers will directly contact water molecules creating a.
A And C B And C.
Phospholipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other what property of the. Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water? Web explain why phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Why do the heads of the phospholipids point.
A) Because Of Their Conical Shape And The Attraction Of The Tails To Each Other B) Because Of.
Web why do phospholipids form bilayers? Web why does phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer when mixed with water because they have an end that is. But the phosphate group is hydrophilic, or soluble in water.
Web Phospholipids Form A Bilayer When Mixed With Water, Since The Hydrophilic Head Is Attracted To Water, While The Hydrophobic Tails Reject Water And Tend To.
Ad high quality phosphatidic acid and dspe lipids available for research. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web phospholipids a molecule that is a part of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head (phosphate group) and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.(2. Web phospholipids form a bilayer when mixed with water, since the hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tails reject water and tend to aggregate with.