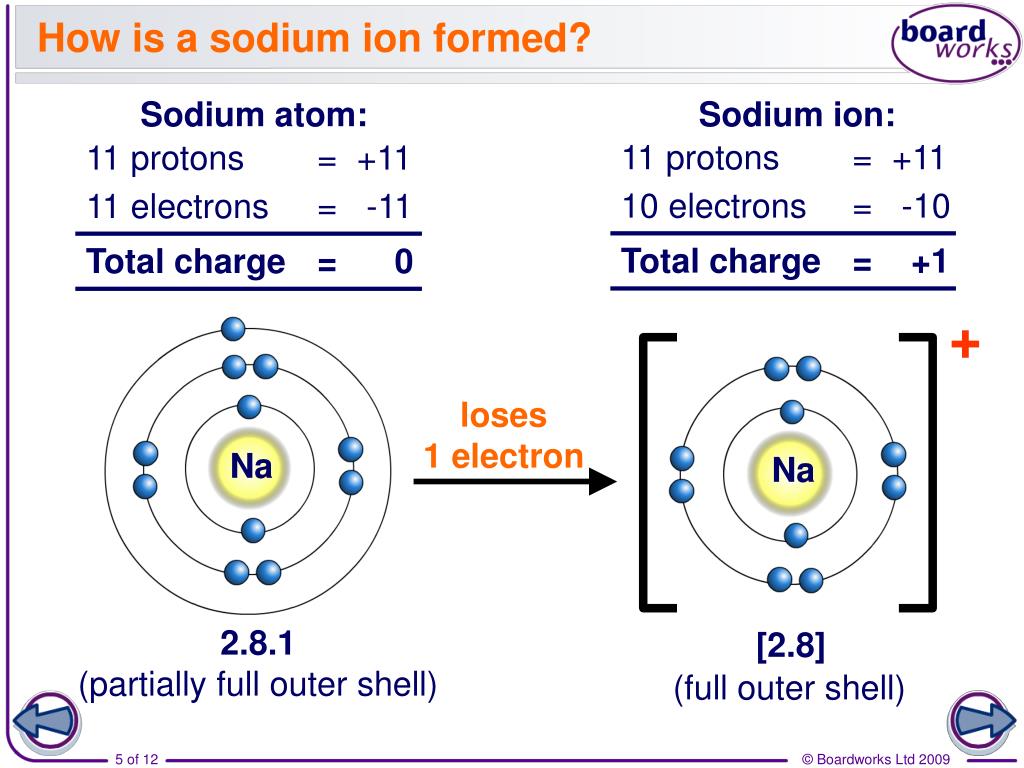
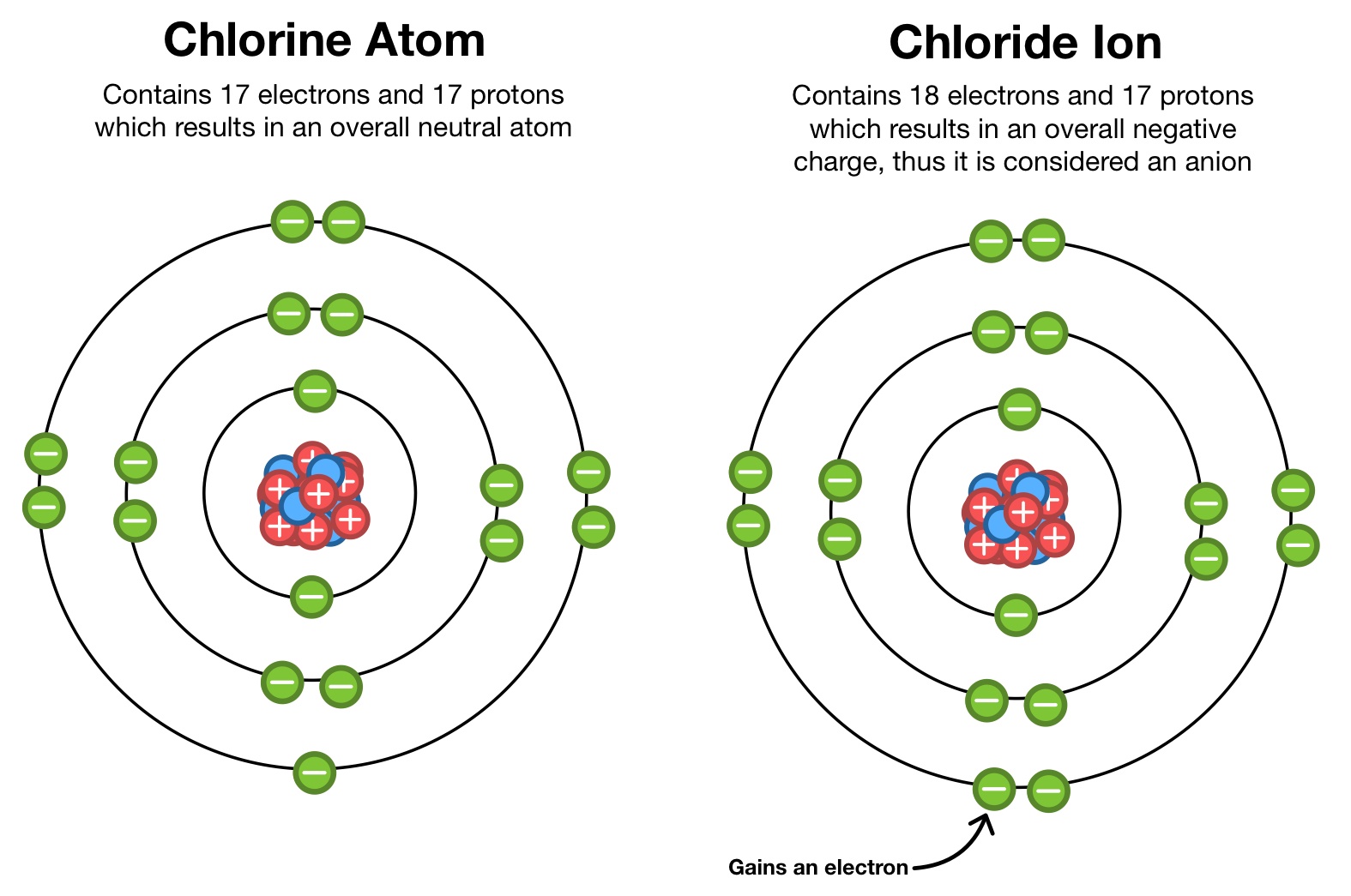
How Does A Positive Ion Form
How Does A Positive Ion Form - Web formation of ions in ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom (and thus the element's identity) remains unchanged. Web what is the proper definition of ions? Web a positive ion forms when an atom loses one or more valence electron. The transfer and sharing of electrons among atoms govern the chemistry of the. This gives the metal ion a filled valence shell. All electrons in the outer energy level are lost. Electrostatics explains why this happens: Lithium has 3 electrons, so. For example, a neutral sodium atom contains electrons in three main energy levels, n=1, n=2, n=3. Electrons, however, can be added to atoms by transfer from other atoms, lost by transfer to other atoms, or shared with other atoms.
Opposite charges attract and like charges repel. These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ). For example, let's look at lithium and fluorine: An ion is a charged atom or molecule. It has one valence electron in the n = 3 energy level. Web positive ions are formed by atoms or molecules suffering an inelastic collision with an energetic electron in which an electron is lost from the atom or molecule (electron impact ionization). Many common materials contain these ions. They form through ionic bonding. The most commonly formed cations of the representative elements are those that involve the loss of all of the valence electrons. It has one electron in its valence shell, which makes it unstable.
Web propulsion how does solar electric propulsion (ion propulsion) work? Consider the alkali metal sodium ( na). Electrons in the outer level. Electrostatics explains why this happens: These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ). Web cations are the positive ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons. Web what is the proper definition of ions? Web at r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower potential energy) than they are at an infinite internuclear distance. Web positive ions are formed by atoms or molecules suffering an inelastic collision with an energetic electron in which an electron is lost from the atom or molecule (electron impact ionization). It has one electron in its valence shell, which makes it unstable.
3.2 Ions The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
An atom can acquire a positive charge or a negative charge depending on whether the number of electrons Web jun 3, 2018 see below. For example, let's look at lithium and fluorine: Web formation of ions in ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom (and thus the element's identity) remains unchanged. Web what is the proper definition of ions?
5.2.1 Formation of Ion Revision.my
The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. Web propulsion how does solar electric propulsion (ion propulsion) work? To form a negative ion it must gain the electrons lost by the cation. It has one valence electron in the n = 3 energy level. The.
PPT How do atoms form ions? PowerPoint Presentation ID7021047
For example, let's look at lithium and fluorine: These ions are positive because they contain more protons. Web at r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower potential energy) than they are at an infinite internuclear distance. All electrons in the outer energy level are lost. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and.
NH4+ Lewis Structure (Ammonium Ion) Math, Lewis, Positivity
When oppositely charged ions are brought Web a positive ion forms when an atom loses one or more valence electron. It has one valence electron in the n = 3 energy level. These ions are positive because they contain more protons. Web if there are more electrons, the atom will form a negative ion, but if the atom has more.
Ions
For example, let's look at lithium and fluorine: The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. An ion is a charged atom or molecule. Consider the alkali metal sodium ( na). The degree of ionization of the plasma depends strongly on the electron density and.
What happens if an atom is not neutral? Socratic
An atom can acquire a positive charge or a negative charge depending on whether the number of electrons Web positive ions are formed by atoms or molecules suffering an inelastic collision with an energetic electron in which an electron is lost from the atom or molecule (electron impact ionization). Web at r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower.
Molecular and Ionic Compounds Chemistry I
Web propulsion how does solar electric propulsion (ion propulsion) work? They form through ionic bonding. The ions are positive, because they have more protons than electrons the ions formed have. Ions migrate under the influence of an electrical field and are the conductors of electric current in electrolytic cells. Web a positive ion forms when an atom loses one or.
Ions Types, Summary, Classification & Facts
All electrons in the outer energy level are lost. Web forming positive ions (cations) atoms lose electrons from their outer shell when they form positive ions, called cations. They form through ionic bonding. An ion is a charged atom or molecule. Web a positive ion is formed when an atom of a metal loses one or more electrons.
What Does Ion Mean? Slanguide
An atom can acquire a positive charge or a negative charge depending on whether the number of electrons Web forming positive ions metal atoms lose electrons from their outer shell when they form ions: Web if there are more electrons, the atom will form a negative ion, but if the atom has more protons, the atom will form a positive.
Ions — Definition & Overview Expii
Web forming positive ions (cations) atoms lose electrons from their outer shell when they form positive ions, called cations. The transfer and sharing of electrons among atoms govern the chemistry of the. Web cations are the positive ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons. Web positive ions are formed by atoms or molecules suffering an inelastic collision.
4 Comments ( 106 Votes) Upvote Downvote Flag
Web if there are more electrons, the atom will form a negative ion, but if the atom has more protons, the atom will form a positive ion. Although the number of protons does not change in the ion, there is an excess number of protons over electrons which produces the positive charge. Electrons in the outer level. An ion is a charged atom or molecule.
It Has One Electron In Its Valence Shell, Which Makes It Unstable.
The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. Web forming positive ions metal atoms lose electrons from their outer shell when they form ions: For example, let's look at lithium and fluorine: They form through ionic bonding.
Web At R0, The Ions Are More Stable (Have A Lower Potential Energy) Than They Are At An Infinite Internuclear Distance.
Examples of positive ions positive ions are typically metals or act like metals. Web jun 3, 2018 see below. Web cations are the positive ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons. These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ).
The Ions Are Positive, Because They Have More Protons Than Electrons The Ions Formed Have.
Web positive ions are formed by atoms or molecules suffering an inelastic collision with an energetic electron in which an electron is lost from the atom or molecule (electron impact ionization). Ions migrate under the influence of an electrical field and are the conductors of electric current in electrolytic cells. The most commonly formed cations of the representative elements are those that involve the loss of all of the valence electrons. All electrons in the outer energy level are lost.