How Does Land Breeze Form
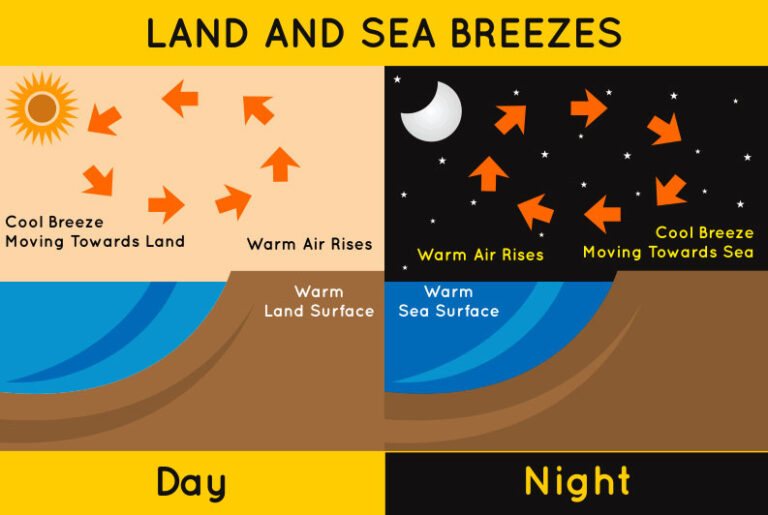
How Does Land Breeze Form - In simple words a land breeze is the flow of wind from the land towards the sea. Web infographic explaining the formation of land breezes. Web land breeze formation of fog occurs when warm air over the sea is cooled as cold air from the land moves over it. A land breeze is a type of wind that blows from the land to the ocean. The speed of sea breeze is fast. A land wind occurs at night, whereas a sea breeze occurs during the day. We can thus categorize the breeze into two types,. Web like all winds, land breezes form because of a difference in temperature and air pressure. Sea breeze affect the temperature. Web land and sea breezes develop because of differential heating and cooling of adjacent land and water surfaces.
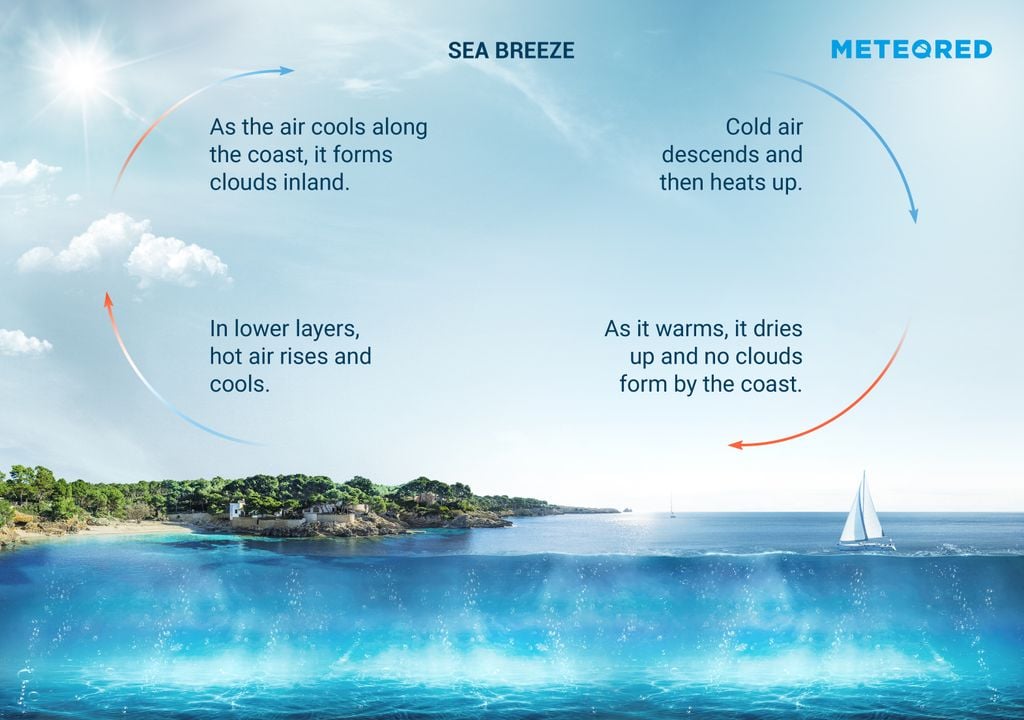
The land cools more quickly than the ocean, cooling the air above it. Web after land again becomes cooler than the water, a land breeze becomes well developed by 0300 lst and reaches its maximum intensity near 0600 lst. A sea breeze is a wind blowing from the water onto the land. Web land breeze formation of fog occurs when warm air over the sea is cooled as cold air from the land moves over it. A land wind occurs at night, whereas a sea breeze occurs during the day. Web like all winds, land breezes form because of a difference in temperature and air pressure. The cold air carries moisture, which condenses as it. The speed of sea breeze is fast. Therefore, the air above the sea will be warmer, and consequently, it will be less dense and will rise, which. Sea breeze affect the temperature.
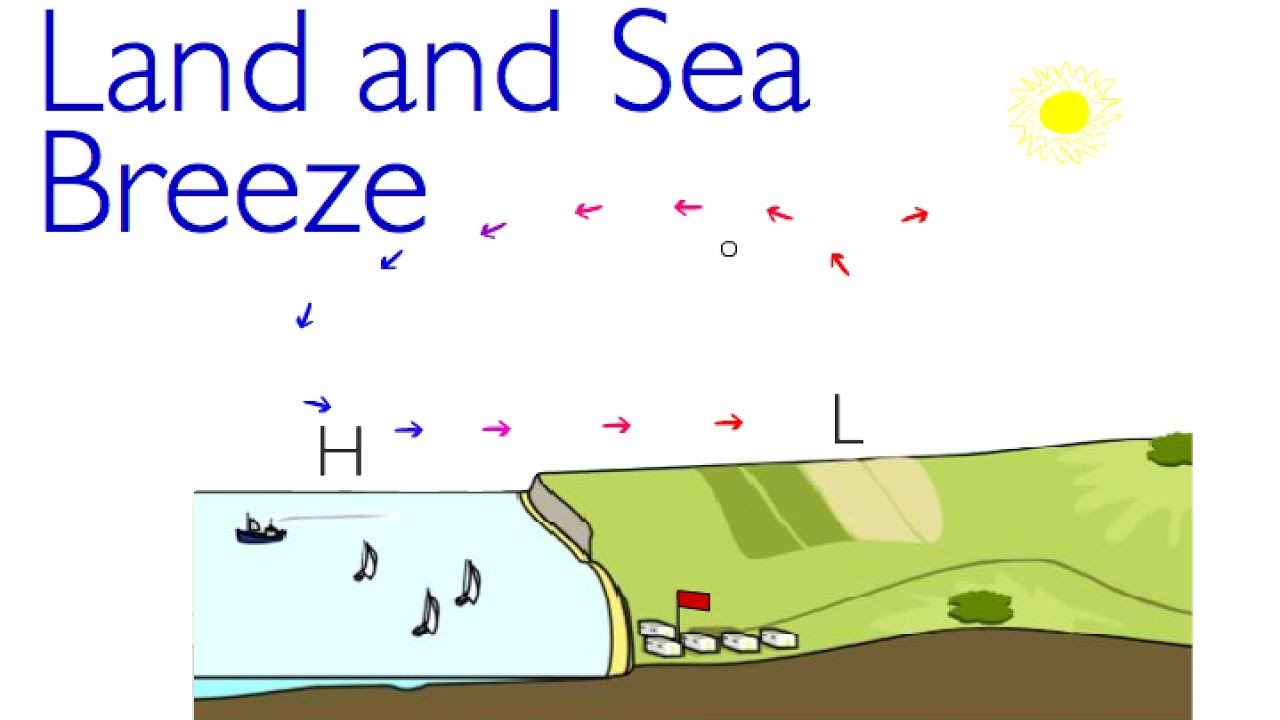
These breezes occur where large bodies of land and water meet. Web land breezes result in the formation and development of clouds. Land breeze does not affect the temperature in any way. Web how does a land breeze form? Therefore, the air above the sea will be warmer, and consequently, it will be less dense and will rise, which. When there is a temperature difference between the land surface and the ocean, winds. Web land and sea breezes develop because of differential heating and cooling of adjacent land and water surfaces. We can thus categorize the breeze into two types,. The warmer air above the. Web a sea breeze front may develop between the warm inland air and the cool sea air.
Phenomena Related to Specific Heat Capacity Land Breeze SPM Physics
Web breeze refers to the moderate or mild wind. The breeze that blows from the land toward the sea after sunset. The speed of sea breeze is fast. Web after land again becomes cooler than the water, a land breeze becomes well developed by 0300 lst and reaches its maximum intensity near 0600 lst. The cold air carries moisture, which.
Land Breeze and Sea Breeze Definitions, Differences and Diagrams
Land breeze does not affect the temperature in any way. The cold air carries moisture, which condenses as it. The different rates at which land and water heat and. Web land and sea breezes develop because of differential heating and cooling of adjacent land and water surfaces. Web breeze refers to the moderate or mild wind.
Land BreezeSea Breeze
Web a sea breeze front may develop between the warm inland air and the cool sea air. In simple words a land breeze is the flow of wind from the land towards the sea. The breeze that blows from the land toward the sea after sunset. Web how does a land breeze form? Web breeze refers to the moderate or.
Sea Breeze And Land Breeze Worksheet Pdf
Web a land breeze is a breeze blowing from land out toward a body of water. The land cools more quickly than the ocean, cooling the air above it. The different rates at which land and water heat and. The breeze that blows from the land toward the sea after sunset. Web offshore winds are referred to as a land.
How do sea and land breezes occur?
When there is a temperature difference between the land surface and the ocean, winds. Web a land breeze is a breeze blowing from land out toward a body of water. A sea breeze is a wind blowing from the water onto the land. Web land breezes result in the formation and development of clouds. The different rates at which land.
PPT LAND BREEZE PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID512674
We can thus categorize the breeze into two types,. The land cools more quickly than the ocean, cooling the air above it. Web a sea breeze front may develop between the warm inland air and the cool sea air. The cold air carries moisture, which condenses as it. Water has a greater heat capacity than land, i.e.
How Mountain and Sea Breezes Affect Weather
This front is responsible for the abundant precipitation in florida. The breeze that blows from the land toward the sea after sunset. Web land and sea breezes develop because of differential heating and cooling of adjacent land and water surfaces. Water has a greater heat capacity than land, i.e. Web land breezes result in the formation and development of clouds.
SECURE SYNOPSIS 24 March 2020 INSIGHTSIAS
Land breezes come from different surfaces’ abilities to retain heat. Web like all winds, land breezes form because of a difference in temperature and air pressure. When there is a temperature difference between the land surface and the ocean, winds. These breezes occur where large bodies of land and water meet. The speed of sea breeze is fast.
Land breeze Definition, Diagram, & Facts Britannica
Web like all winds, land breezes form because of a difference in temperature and air pressure. Web after land again becomes cooler than the water, a land breeze becomes well developed by 0300 lst and reaches its maximum intensity near 0600 lst. The breeze that blows from the land toward the sea after sunset. Water has a greater heat capacity.
Download Diagram Showing Sea And Land Breeze for free Earth drawings
Web a sea breeze front may develop between the warm inland air and the cool sea air. Web land breeze formation of fog occurs when warm air over the sea is cooled as cold air from the land moves over it. Web a land breeze is a breeze blowing from land out toward a body of water. Web infographic explaining.
Web A Land Breeze Is A Breeze Blowing From Land Out Toward A Body Of Water.
Water has a greater heat capacity than land, i.e. Sea breeze affect the temperature. Web land breezes result in the formation and development of clouds. Web the speed of land breeze is slow.
We Can Thus Categorize The Breeze Into Two Types,.
Web infographic explaining the formation of land breezes. Web land breeze formation of fog occurs when warm air over the sea is cooled as cold air from the land moves over it. The cold air carries moisture, which condenses as it. A sea breeze is a wind blowing from the water onto the land.
Therefore, The Air Above The Sea Will Be Warmer, And Consequently, It Will Be Less Dense And Will Rise, Which.
This front is responsible for the abundant precipitation in florida. Web offshore winds are referred to as a land breeze, whereas onshore winds are referred to as a sea breeze. Sea breezes here develop on. When there is a temperature difference between the land surface and the ocean, winds.
In Simple Words A Land Breeze Is The Flow Of Wind From The Land Towards The Sea.
Web breeze refers to the moderate or mild wind. Web a sea breeze front may develop between the warm inland air and the cool sea air. The speed of sea breeze is fast. Web like all winds, land breezes form because of a difference in temperature and air pressure.