Where Do Most Local Potentials Form In A Neuron
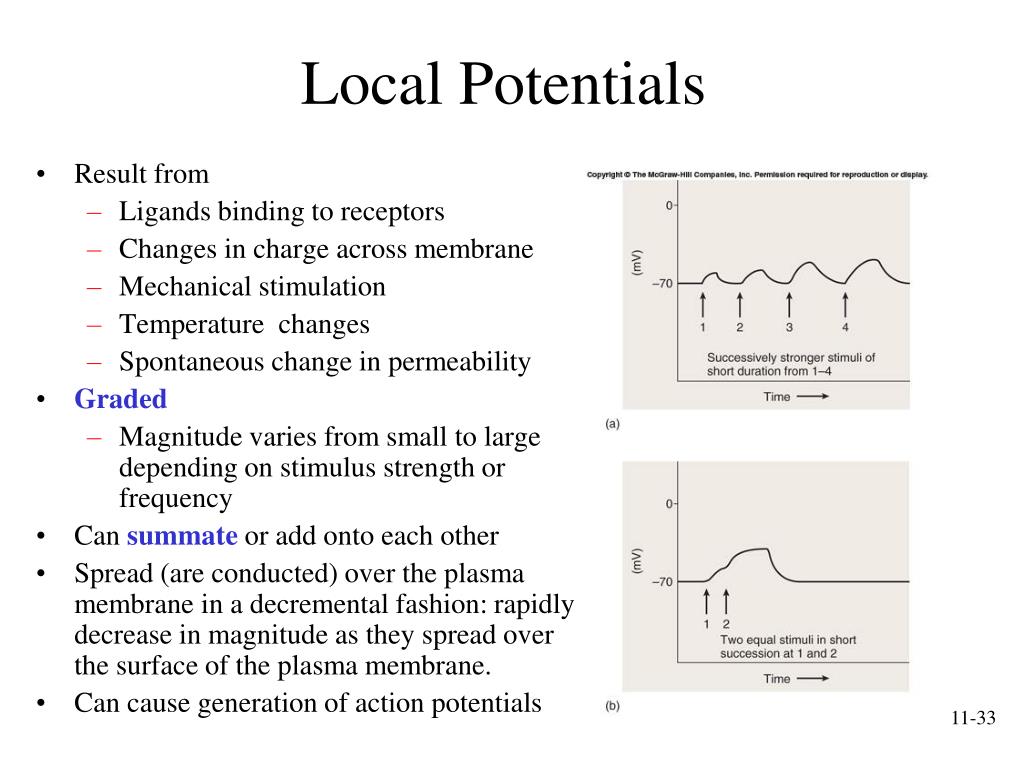
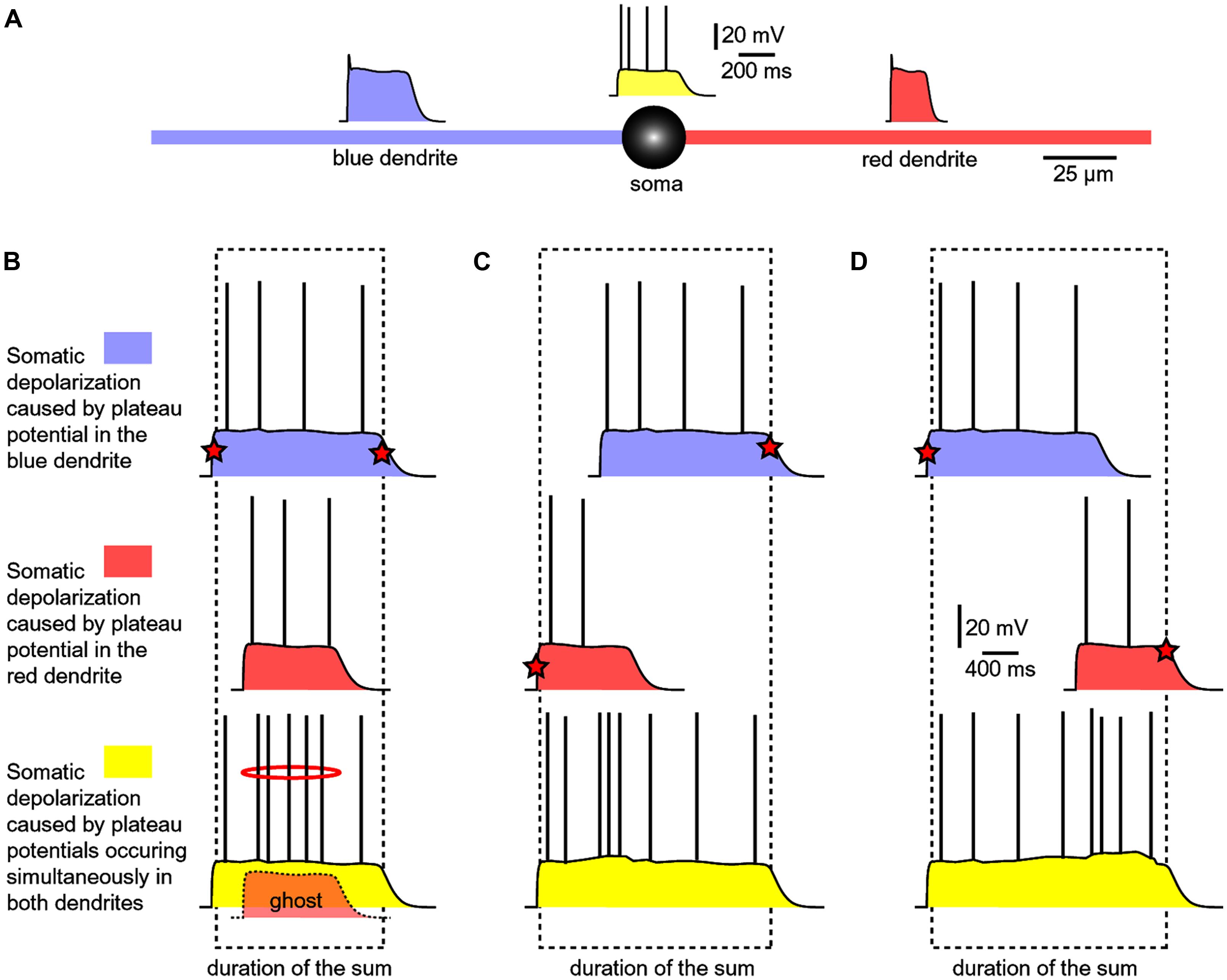
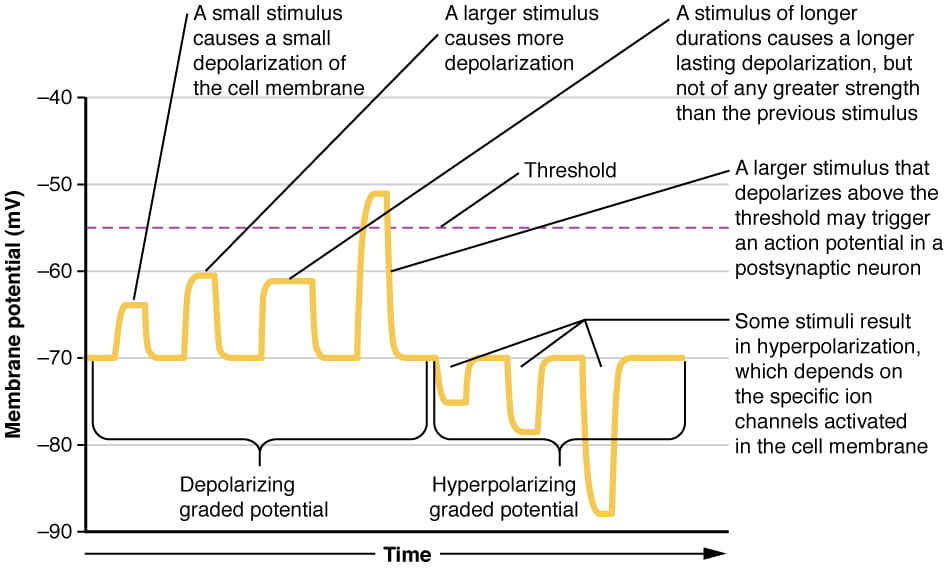
Where Do Most Local Potentials Form In A Neuron - Web beginning at the resting potential of a neuron (for instance, −75 mv), a local potential can be of any grade up to the threshold potential (for instance, −58 mv). Web most local potentials in a neuron form at the dendrites and cell body (soma). Local potentials, or graded potentials, are small changes that either repolarize or depolarize the membrane. Which of the following events happens next? The answer is the cell membrane. Web three types of local potentials are (1) receptor (or generator) potential, triggered by the action of a sensory stimulus on a sensory receptor; They allow the brain and spinal cord to communicate with muscles, organs, and glands all over the body. (1) a stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to depolarize toward the threshold. Potassium where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web motor neurons are crucial for voluntary and involuntary movements.
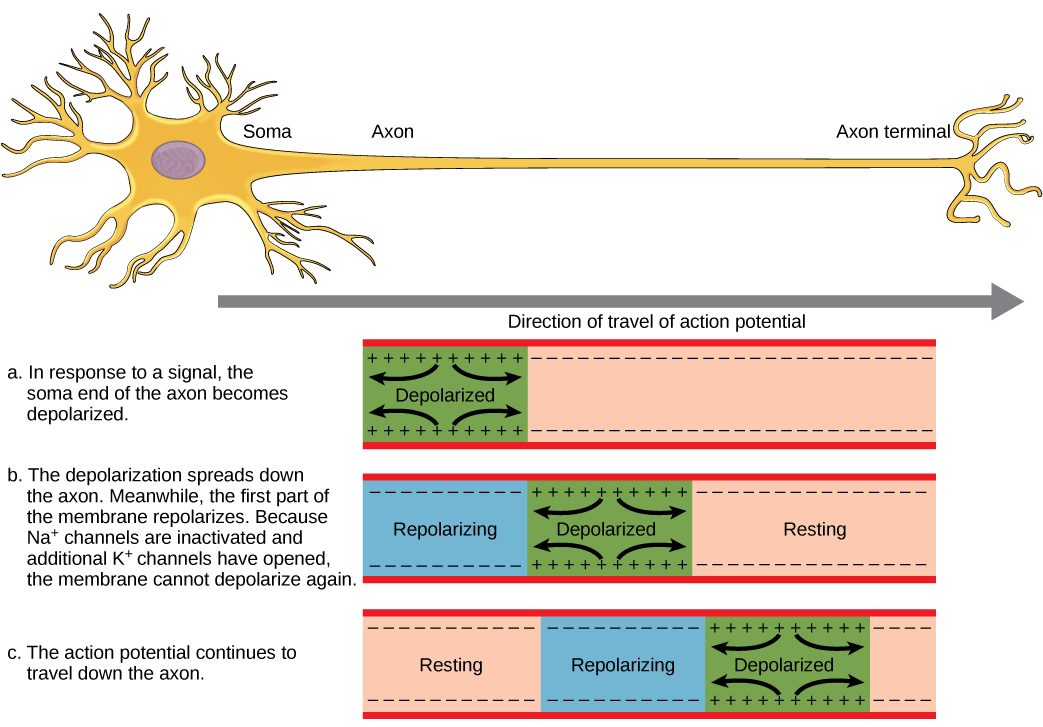
Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of. Local potentials are small changes in the membrane potential of a neuron that. Neurons complete this task using a process called action. The dendrites what is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain? Web motor neurons are crucial for voluntary and involuntary movements. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web so, where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses.
Synapses are locations where neurons can pass these electrical and chemical. Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane. The dendrites what is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain? Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses. The dendrites in a neuron, the opening of sodium gates typically leads to _____. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web most local potentials in a neuron form at the dendrites and cell body (soma). Local potentials are small changes in the membrane potential of a neuron that. Web three types of local potentials are (1) receptor (or generator) potential, triggered by the action of a sensory stimulus on a sensory receptor;
PPT Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue PowerPoint Presentation
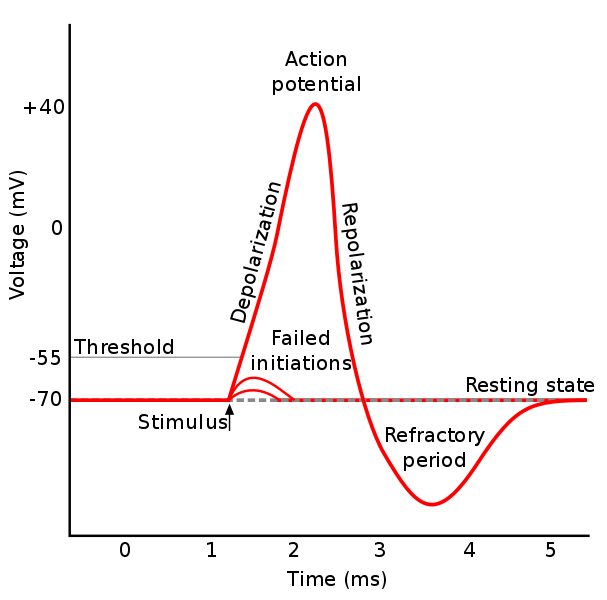
Web an action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? They allow the brain and spinal cord to communicate with muscles, organs, and glands all over the body. Dendrites a neuron recieves a.
Labeled Neuron Diagram Science Trends
Web so, where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web a neuron's function involves sending electrical impulses and chemical signals to and from the brain. Synapses are locations where neurons can pass these electrical and chemical.
Neuron stimulated by a chemical, local potential generated at plasma
The answer is the cell membrane. Web most local potentials form in the dendrites of a neuron. Potassium where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Web three types of local potentials are (1) receptor (or generator) potential, triggered by the action of a sensory stimulus on a sensory.
Graded and action potentials in neurons YouTube
Web action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses. Which of the following events happens next? Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane. The cell membrane is a specialized structure that separates the cell from its. Web a neuron's.
Neurons Organismal Biology
Web most local potentials in a neuron form at the dendrites and cell body (soma). Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of. Web motor neurons are crucial for voluntary and involuntary movements. The dendrites in a neuron, the opening of sodium gates typically leads to _____.
Action Potential In Plants / Neuron action potential Osmosis The
Web motor neurons are crucial for voluntary and involuntary movements. Web where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Dendrites a neuron recieves a stimulus. Local potentials, or graded potentials, are small changes that either repolarize or depolarize the membrane. The answer is the cell membrane.
neuroscience Explanatory gaps in the formation and propagation of
Local potentials are small changes in the membrane potential of a neuron that. Web the formation of an action potential can be divided into five steps: Web beginning at the resting potential of a neuron (for instance, −75 mv), a local potential can be of any grade up to the threshold potential (for instance, −58 mv). Web an action potential.
Do graded potentials only occur in the dendrities of the neuron
Web a neuron's function involves sending electrical impulses and chemical signals to and from the brain. Local potentials, or graded potentials, are small changes that either repolarize or depolarize the membrane. Neurons complete this task using a process called action. They allow the brain and spinal cord to communicate with muscles, organs, and glands all over the body. The answer.
neurophysiology Behaviour of neuron when membrane potential is
Which of the following events happens next? Web most local potentials in a neuron form at the dendrites and cell body (soma). Web an action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Web action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses. Synapses are locations where neurons can pass these electrical.
Neurons Organismal Biology
Web beginning at the resting potential of a neuron (for instance, −75 mv), a local potential can be of any grade up to the threshold potential (for instance, −58 mv). The answer is the cell membrane. Web a neuron's function involves sending electrical impulses and chemical signals to and from the brain. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of..
Web Where Do Most Local Potentials Form In A Neuron?
Which of the following events happens next? The cell membrane is a specialized structure that separates the cell from its. Web an action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Local potentials, or graded potentials, are small changes that either repolarize or depolarize the membrane.
Web The Formation Of An Action Potential Can Be Divided Into Five Steps:
Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane. Potassium where do most local potentials form in a neuron? Local potentials are small changes in the membrane potential of a neuron that. The dendrites in a neuron, the opening of sodium gates typically leads to _____.
The Answer Is The Cell Membrane.
Web most local potentials form in the dendrites of a neuron. Web motor neurons are crucial for voluntary and involuntary movements. The dendrites what is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain? Synapses are locations where neurons can pass these electrical and chemical.
Web Where Do Most Local Potentials Form In A Neuron?
Neurons complete this task using a process called action. Web three types of local potentials are (1) receptor (or generator) potential, triggered by the action of a sensory stimulus on a sensory receptor; They allow the brain and spinal cord to communicate with muscles, organs, and glands all over the body. Web most local potentials in a neuron form at the dendrites and cell body (soma).