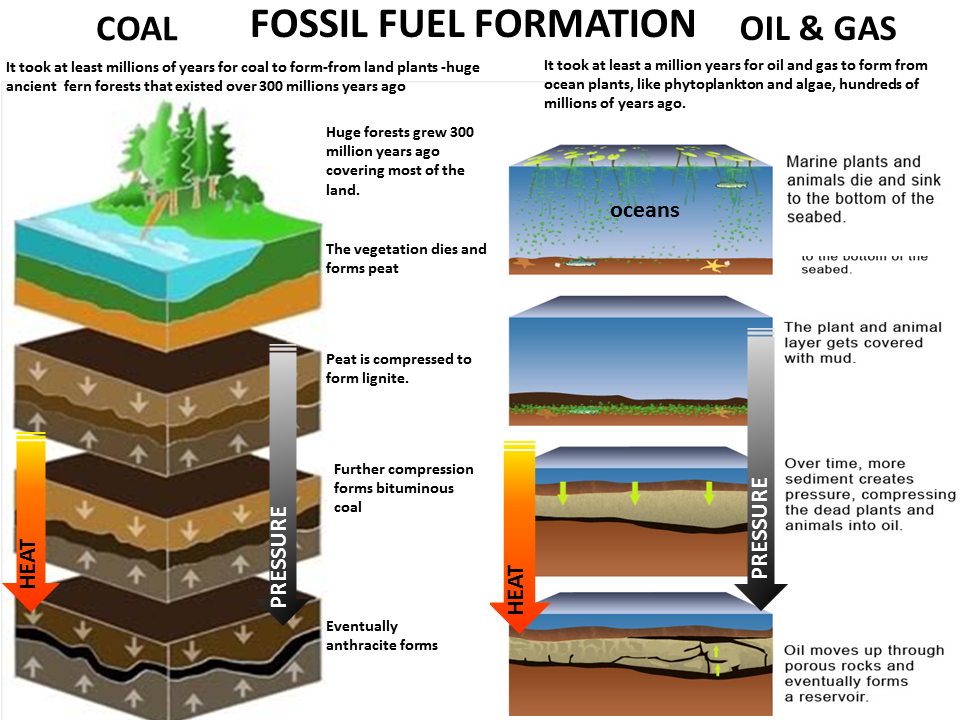
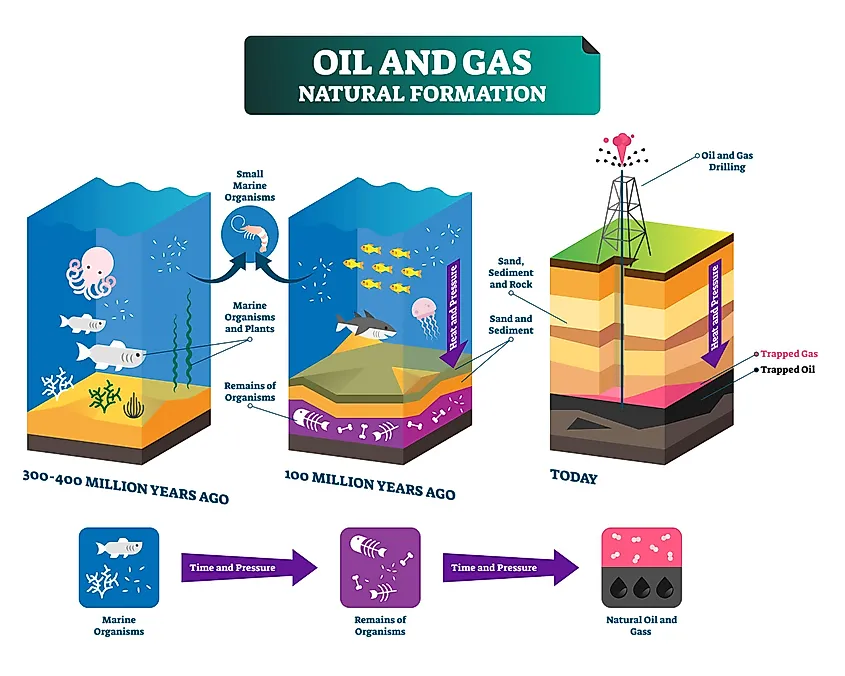
Which Best Describes How Fossil Fuels Form
Which Best Describes How Fossil Fuels Form - Fossil fuels are a finite resource, meaning that they cannot be replaced once extracted from the ground. Fossil fuels include coal, petroleum, and natural gas. This energy was originally captured. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. Web the statement best describes the fossil fuels are decayed organisms are compressed underground. Web which best describes how fossil fuels form? These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains. Coal was formed when large plants in swamps died 300 million years ago (before the dinosaurs). Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy.
Fossil fuels are a finite resource, meaning that they cannot be replaced once extracted from the ground. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. Fossil fuels include coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Web coal , oil and gas are called ‘fossil fuels’ because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of dead prehistoric plants and animals. Web fossil fuel is a general term for buried combustible geologic deposits of organic materials, formed from decayed plants and animals that have been converted to crude oil, coal,. These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed. Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago. Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy. There’s even an oil company,. Coal was formed when large plants in swamps died 300 million years ago (before the dinosaurs).
Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of years ago. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. This has contributed to global warming. Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy. Web examples of fossil fuels. Over millions of years, this vegetation was buried under water. Fossil fuels are a finite resource, meaning that they cannot be replaced once extracted from the ground. This fossil fuel is formed when land vegetation buried deep by sediments in the ground starts to decompose slowly through anaerobic. In 2015, 80 per cent of energy consumed in the world came. Fossil fuels include coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
PPT How do fossil fuels form and how are they extracted? PowerPoint
In 2015, 80 per cent of energy consumed in the world came. Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy. Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt which is a major greenhouse gas and the primary source of pollution. These remains are.
My Newsroom Physics Energy Conversion and Fossil Fuels
Coal was formed when large plants in swamps died 300 million years ago (before the dinosaurs). This has contributed to global warming. In 2015, 80 per cent of energy consumed in the world came. Web which best describes how fossil fuels form? These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed.
How Do Fossil Fuels Form Apex
Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt which is a major greenhouse gas and the primary source of pollution. Web the statement best describes the fossil fuels are decayed organisms are compressed underground. These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed. Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of.
How Fossil Fuels Are Formed YouTube
Over millions of years, this vegetation was buried under water. Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt which is a major greenhouse gas and the primary source of pollution. Natural gas is burned to form coal and oil. Web which best describes how fossil fuels form? Web fossils are the remains of plants and animals, and fossil fuels are decomposed.
Fossil Fuel Divestment Effective Assets
Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago. Natural gas is burned to form coal and oil. These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed. Web the statement best describes the fossil fuels are decayed organisms are.
How fossil fuels are formed Storyboard by 200d0eaa
Fossil fuels are formed from the remains. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. This energy was originally captured. Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of years ago. Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago.
Fossil Fuel Examples and Uses
Fossil fuels are a finite resource, meaning that they cannot be replaced once extracted from the ground. This has contributed to global warming. Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. Fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide when burnt.
Are Fossil Fuels Really Bad for the Environment? The Earth Project
Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago. In 2015, 80 per cent of energy consumed in the world came. Web one of the most widespread beliefs about fossil fuels — oil, natural gas and coal — is that these substances started out as dinosaurs..
Fossil Fuels WorldAtlas
Over millions of years, this vegetation was buried under water. Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of years ago. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains. Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago.
Which Best Describes How Fossil Fuels Form
Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of years ago. Web one of the most widespread beliefs about fossil fuels — oil, natural gas and coal — is that these substances started out as dinosaurs. Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as.
Web Which Best Describes How Fossil Fuels Form?
This has contributed to global warming. Fossil fuels include coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Web the statement best describes the fossil fuels are decayed organisms are compressed underground. Web fossils are the remains of plants and animals, and fossil fuels are decomposed plants and animals that form coal, oil, and natural gas.
Web Fossil Fuels Form From The Remains Of Past Organisms.
Web fossil fuel, any of a class of materials of biologic origin occurring within the earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy. Sunlight converts grass to coal and oil. These remains are pressed and heated underground for millions of years until fossil fuels are formed. Natural gas is burned to form coal and oil.
Fossil Fuels Emit Carbon Dioxide When Burnt Which Is A Major Greenhouse Gas And The Primary Source Of Pollution.
In 2015, 80 per cent of energy consumed in the world came. Fossil fuels are a finite resource, meaning that they cannot be replaced once extracted from the ground. Web shale gas is a fossil fuel that formed millions of years ago. Web fossil fuel is a general term for buried combustible geologic deposits of organic materials, formed from decayed plants and animals that have been converted to crude oil, coal,.
Over Millions Of Years, This Vegetation Was Buried Under Water.
Web examples of fossil fuels. Web one of the most widespread beliefs about fossil fuels — oil, natural gas and coal — is that these substances started out as dinosaurs. There’s even an oil company,. Web fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy formed from the organic matter of plants and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago.