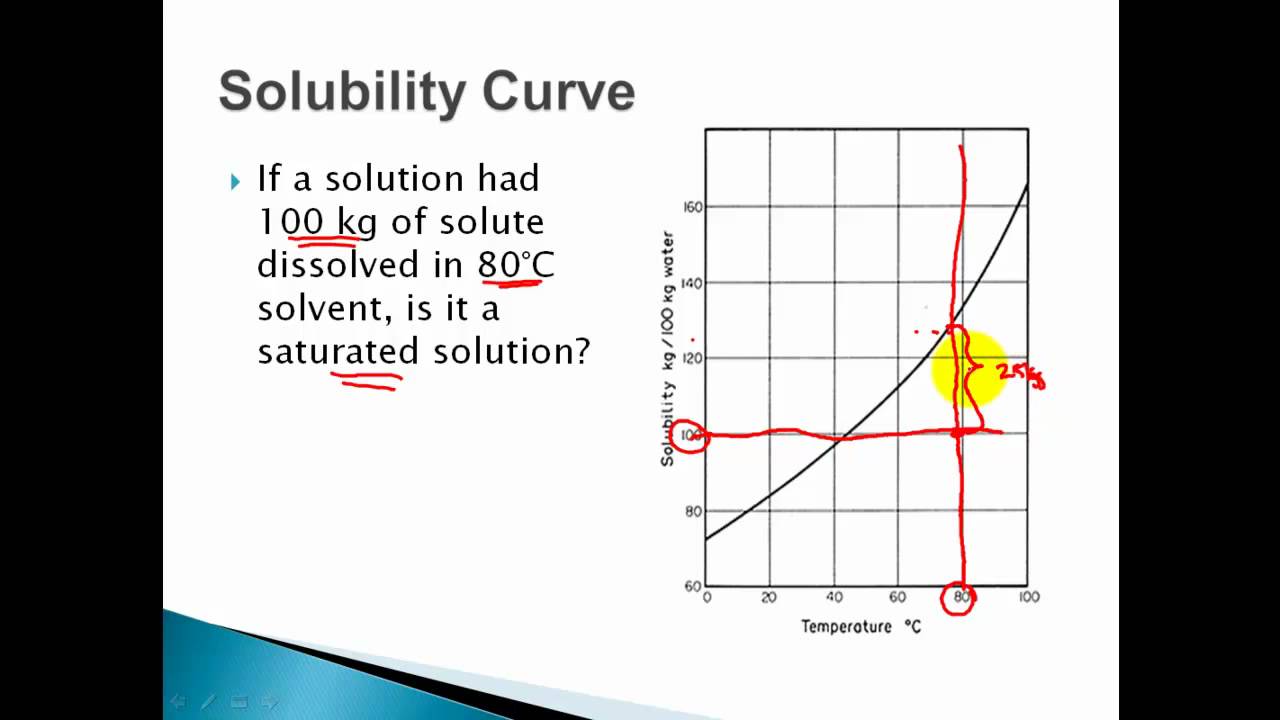
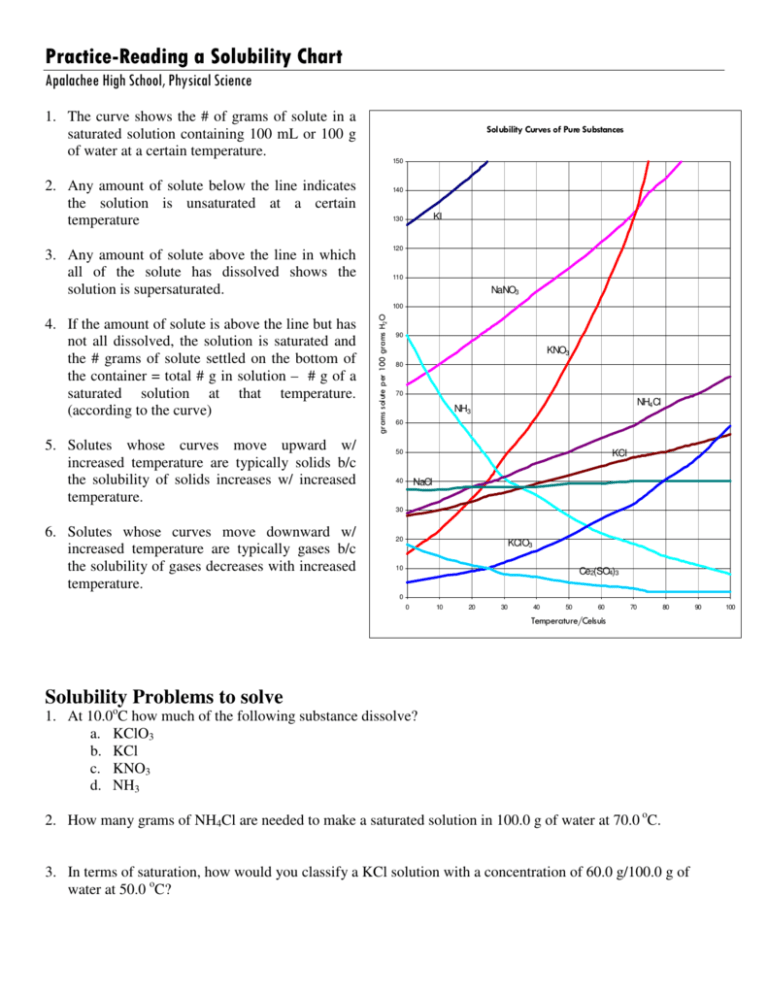
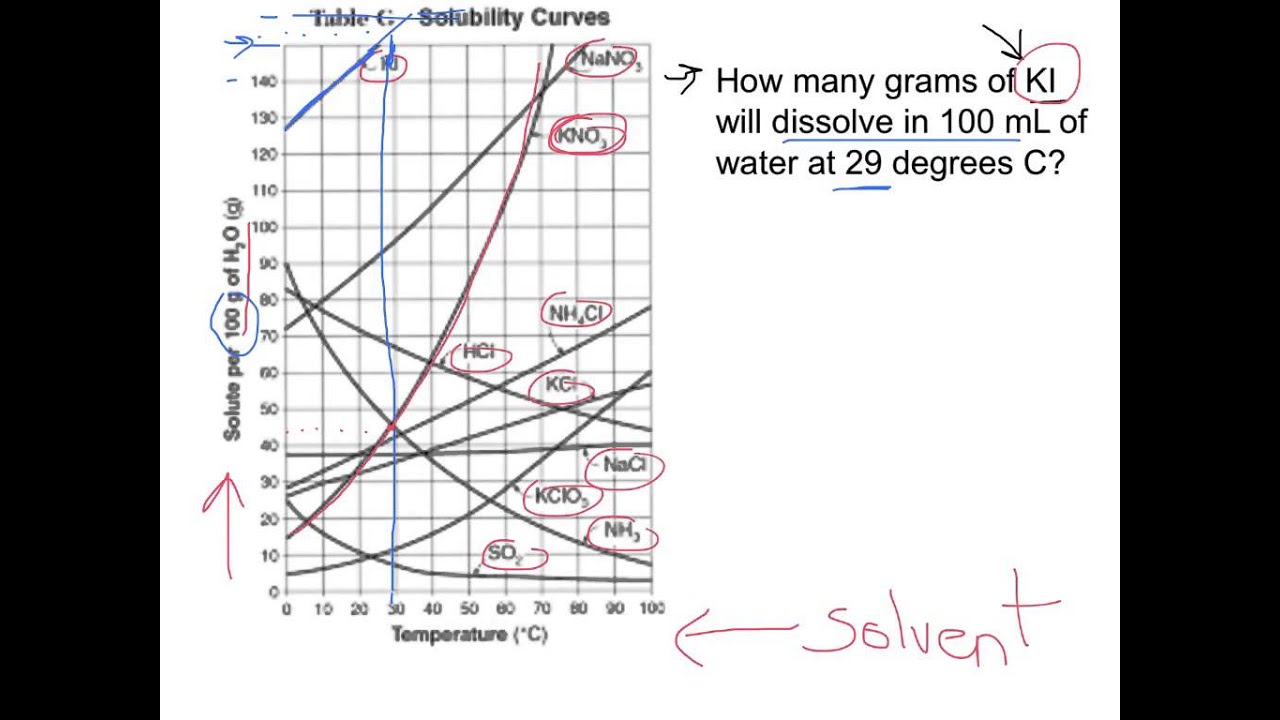
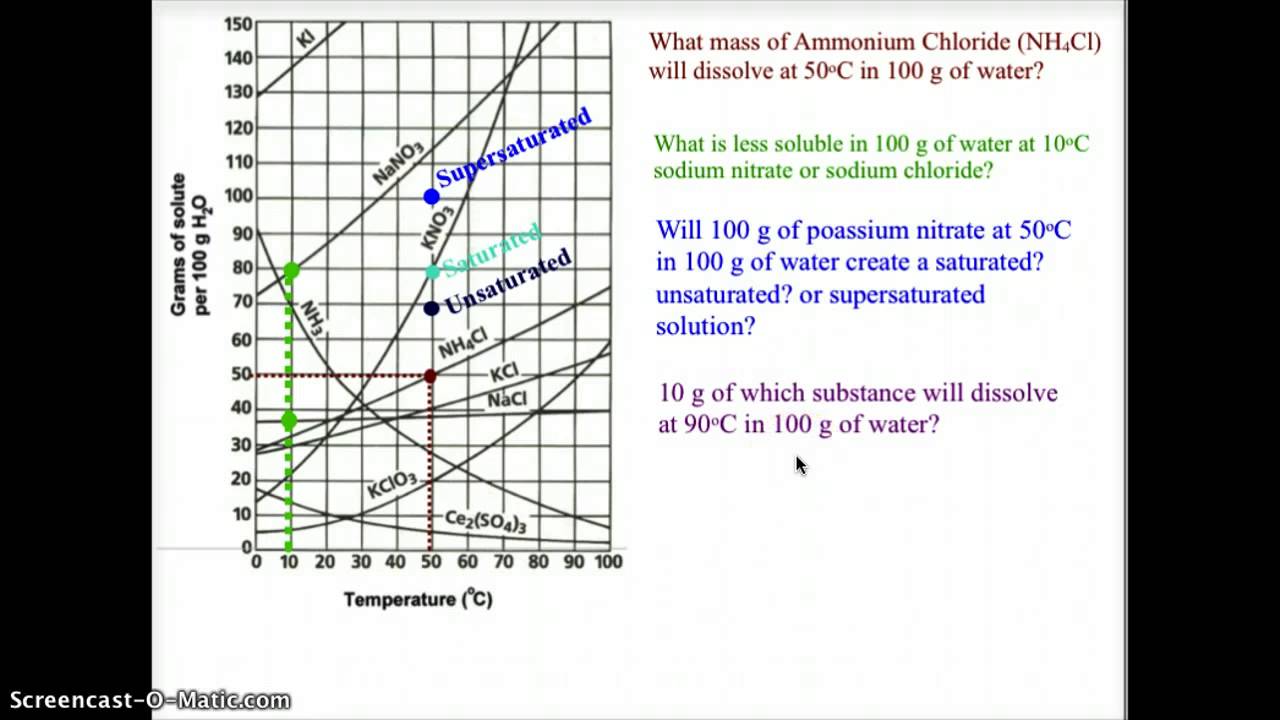
How To Read Solubility Curves
How To Read Solubility Curves - Web learn if a solution is saturated or unsaturated by reading a solubility curve. A solubility curve is a graph of solubility, measured in g/100 g water, against temperature in °c. The solubility curve is a graph that shows how the concentration of a solute. To read the graph, find the line for the substance. From reading a solubility graph, one can determine the mass of solute that can dissolve at specific temperatures,. Web reading solubility curves what is solubility? It contains plenty of examples and practice problems on calculating the solubility of an ionic compound at a. Web solubility curvesare used to show how the solubility of a substance changes with temperature. The curve line drawn on a graph showing the relationship between temperature and solubility of the substance. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 2.
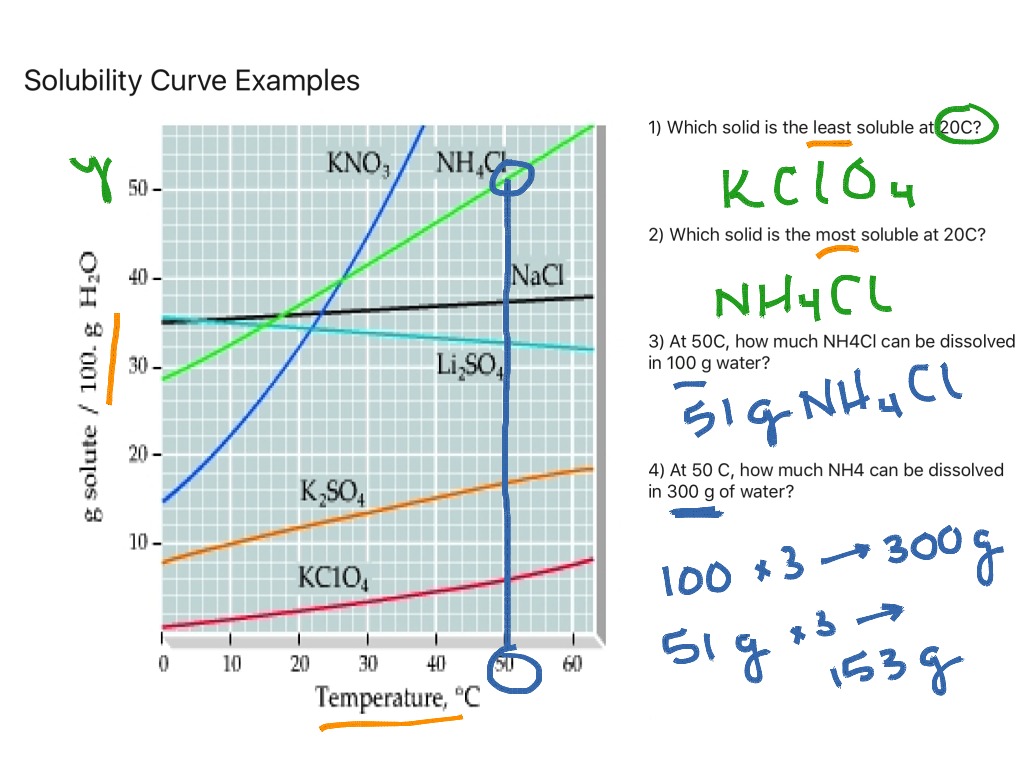
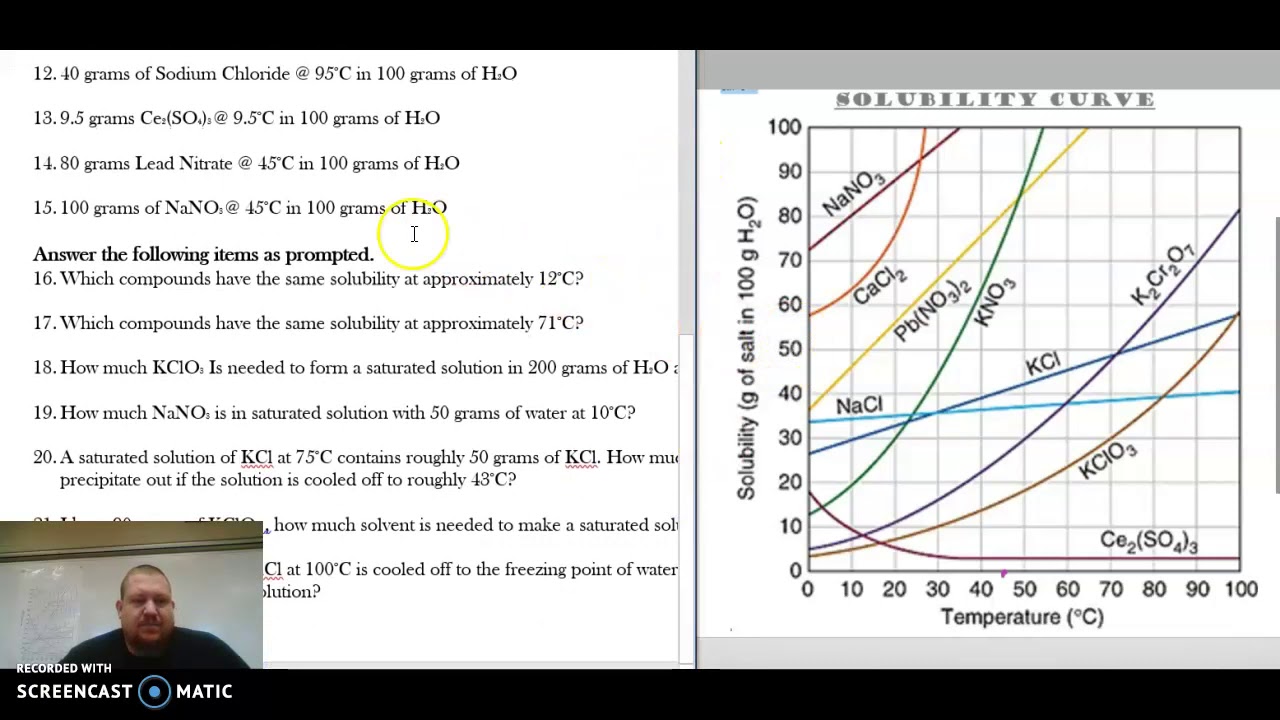
Web how to read a solubility graph. The curve line drawn on a graph showing the relationship between temperature and solubility of the substance. Web the variation in the solubility of any given substance with the change of temperature is shown by the solubility curve. Web a solubility graph is drawn to display the solubility at different temperatures. Learn how to describe a solution with a solubility curve show more. The maximum amount of a substance that will dissolve in a certain amount of solvent at a given temperature is called that substances solubility in that solvent. How much kclwould be able to dissolve in 100 g of water at 50ºc? 2) the ph of the solution at equivalence point is dependent. Solubility curves for more than one substance are often drawn on the same. Web reading solubility curves what is solubility?
What is the likely identity of the unknown?. To read the graph, find the line for the substance. Web how to read a solubility graph. At 40ºc, exactly 64 g of an unknown salt dissolved in 100 g of water. Example questions what mass of solute will dissolve in 100g of water at the following temperatures? Web the graph will typically have a curve that shows the solubility as a function of temperature. 2) the ph of the solution at equivalence point is dependent. 68k views 7 years ago. Web 0:00 / 15:10 solubility curves explained chem academy 33.7k subscribers subscribe 838 94k views 8 years ago solutions in this video i will explain solubility curves. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 1.
Solubility Curves Saturated, Unsaturated, Supersaturated Solutions
To read the graph, find the line for the substance. How much kclwould be able to dissolve in 100 g of water at 50ºc? Learn how to describe a solution with a solubility curve show more. The solubility curve is a graph that shows how the concentration of a solute. What is the likely identity of the unknown?.
PracticeReading a Solubility Chart
Web reading solubility curves what is solubility? Both in g/100 ml g / 100 m l of water. To read the graph, find the line for the substance. Web how to read a solubility graph. Web the variation in the solubility of any given substance with the change of temperature is shown by the solubility curve.
Reading solubility curves YouTube
Web how to read a solubility curve 1. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into solubility curves. The curve line drawn on a graph showing the relationship between temperature and solubility of the substance. The solubility curve is a graph that shows how the concentration of a solute. Web the variation in the solubility of any given.
Interpreting Solubility Curves YouTube
I assume both cross solubilities are related to the volume of water used for the initial solution, not of the initial solution volume, i.e. Solubility curves for more than one substance are often drawn on the same. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 2. 2) the ph of the solution at equivalence point is dependent. At 40ºc, exactly 64 g of.
Read Solubility Curve Practice Answers / PPT UNIT 1C Reading
Solubility curves for more than one substance are often drawn on the same. 68k views 7 years ago. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 2. Web how to read a solubility curve 1. Web how to read a solubility graph.
Read Solubility Curve Practice Answers / Hw Solubility Curve Worksheet
Practice reading a solubility graph—part 1. What is the likely identity of the unknown?. Solubility curves for more than one substance are often drawn on the same. A solubility curve is a graph of solubility, measured in g/100 g water, against temperature in °c. I assume both cross solubilities are related to the volume of water used for the initial.
Reading a SolubilityChart.doc Google Docs
Web how to read a solubility curve 1. Web the variation in the solubility of any given substance with the change of temperature is shown by the solubility curve. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 1. Web the graph will typically have a curve that shows the solubility as a function of temperature. 68k views 7 years ago.
Solubility & Solubility Curves Science, Chemistry ShowMe
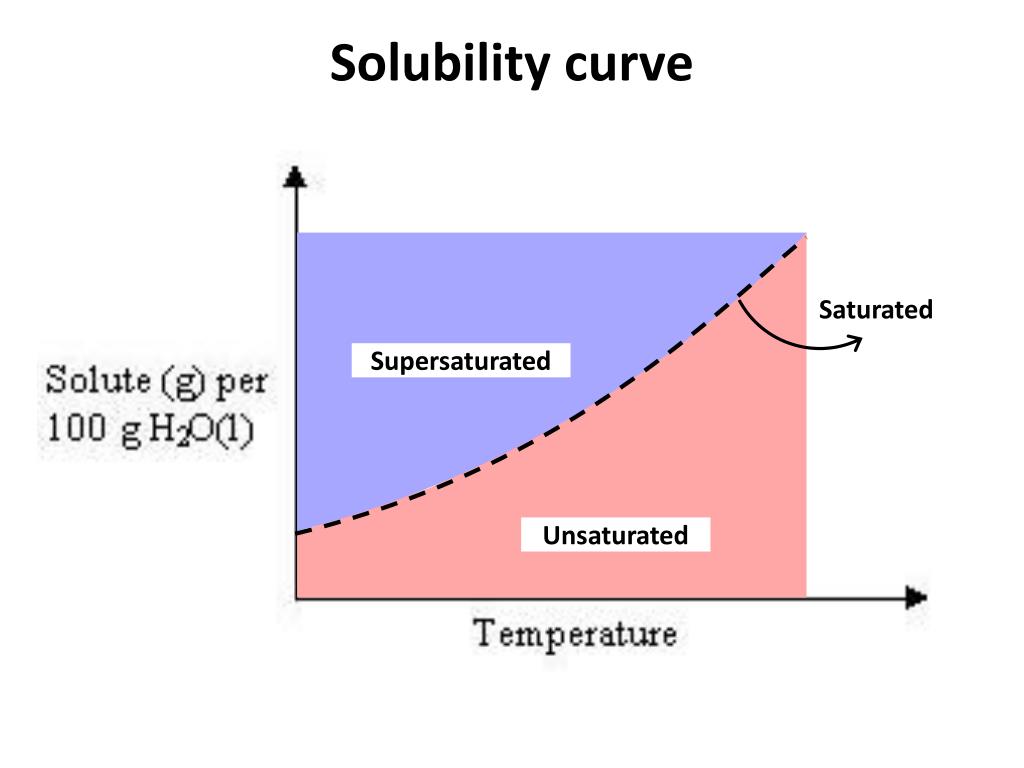
Learn how to describe a solution with a solubility curve show more. 68k views 7 years ago. What is the likely identity of the unknown?. Web reading solubility curves what is solubility? The maximum amount of a substance that will dissolve in a certain amount of solvent at a given temperature is called that substances solubility in that solvent.
PPT Solubility curve PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6497715
Example questions what mass of solute will dissolve in 100g of water at the following temperatures? Web a solubility graph is drawn to display the solubility at different temperatures. Both in g/100 ml g / 100 m l of water. The maximum amount of a substance that will dissolve in a certain amount of solvent at a given temperature is.
Practice Reading Solubility Curve Pt. 1 YouTube
Practice reading a solubility graph—part 1. To read the graph, find the line for the substance. At 40ºc, exactly 64 g of an unknown salt dissolved in 100 g of water. The maximum amount of a substance that will dissolve in a certain amount of solvent at a given temperature is called that substances solubility in that solvent. Web how.
The Solubility Curve Is A Graph That Shows How The Concentration Of A Solute.
What is the likely identity of the unknown?. Web how to read a solubility curve 1. To read the graph, find the line for the substance. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 2.
Both In G/100 Ml G / 100 M L Of Water.
Web the graph will typically have a curve that shows the solubility as a function of temperature. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into solubility curves. Web learn if a solution is saturated or unsaturated by reading a solubility curve. 68k views 7 years ago.
Web Reading Solubility Curves What Is Solubility?
Learn how to describe a solution with a solubility curve show more. Practice reading a solubility graph—part 1. From reading a solubility graph, one can determine the mass of solute that can dissolve at specific temperatures,. Web a solubility graph is drawn to display the solubility at different temperatures.
At 40ºc, Exactly 64 G Of An Unknown Salt Dissolved In 100 G Of Water.
How to read the solubility curve? Example questions what mass of solute will dissolve in 100g of water at the following temperatures? I assume both cross solubilities are related to the volume of water used for the initial solution, not of the initial solution volume, i.e. Solubility curves for more than one substance are often drawn on the same.