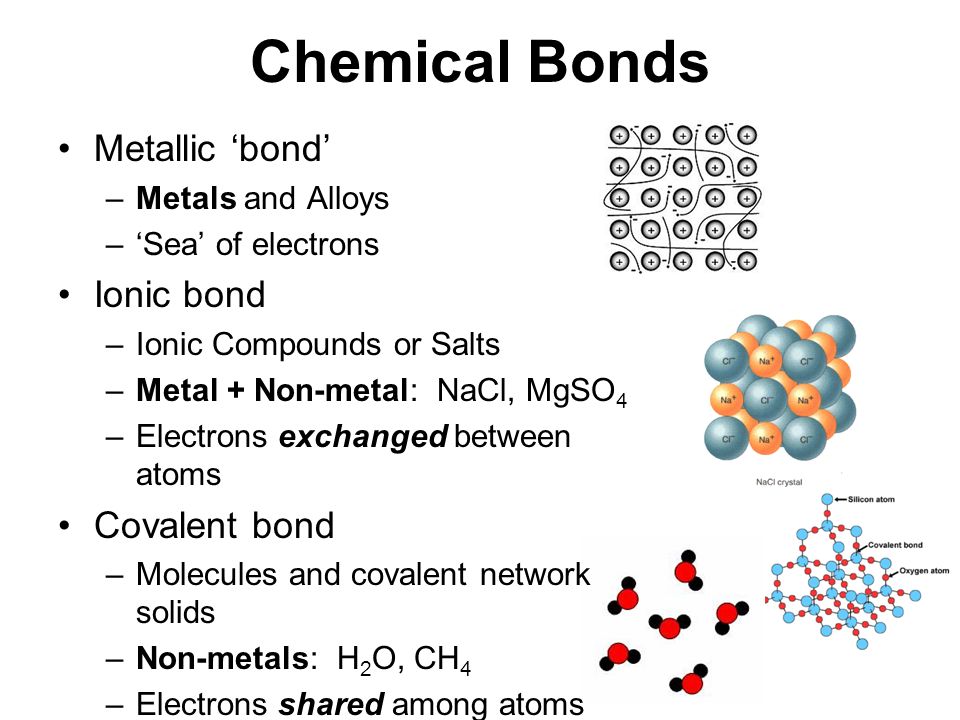
Which Atom Is Most Likely To Form A Metallic Bond
Which Atom Is Most Likely To Form A Metallic Bond - Web a metallic bond is the way that metal atoms are kept together within a metal material. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond similar to a covalent bond. Web when one atom takes an electron away from another and the resulting positive and negative ions are attracted to each other, those atoms have formed an ionic bond. The loss of metallic properties b. Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. The mercurous ion also exhibits metallic and covalent. Which is most likely the result of millions of metal atoms crowding together so that molecular orbitals become combined? Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) aluminum (al) is most likely to form a metallic bond. If atoms have similar electronegativities (the. Web for example, covalently bonded gallium atoms tend to form crystal structures that are held together via metallic bonds.
If atoms have similar electronegativities (the. Web this bonding occurs primarily between nonmetals; Web a metallic bond is the way that metal atoms are kept together within a metal material. Web when one atom takes an electron away from another and the resulting positive and negative ions are attracted to each other, those atoms have formed an ionic bond. Ionic bonding results from the electrostatic attraction of oppositely. Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond get the answers you need, now! Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond similar to a covalent bond.
A kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons. Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) a lead is malleable, so it can be pounded into flat sheets. Web aluminum atom is most likely to form a metallic bond. Web when one atom takes an electron away from another and the resulting positive and negative ions are attracted to each other, those atoms have formed an ionic bond. Web metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized. Web answer:aluminium (al) atom is most likely to form a metallic bond.explanation:a kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons and positively However, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. The loss of metallic properties b. Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond?
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other
The loss of metallic properties b. Web this bonding occurs primarily between nonmetals; Web when one atom takes an electron away from another and the resulting positive and negative ions are attracted to each other, those atoms have formed an ionic bond. Web answer:aluminium (al) atom is most likely to form a metallic bond.explanation:a kind of chemical bonding which generates.
Bonds Between Atoms Sciencetastic!
Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? It has only metallic bonds between the atoms. Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular. Web metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized. Web.
savvychemist Periodicity (2) Melting and boiling points of the
Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular. Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) aluminum (al) is most likely to form a metallic bond. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond get the answers you need, now! Which is most likely the result of millions of metal atoms crowding together.
Metallic Substances (8/12) Atomic Structure NCEA Level 2 Chemistry
Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? However, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? Define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds. A kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons.
Metallic Bond — Formation & Compounds Expii
Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond get the answers you need, now! Web a metallic bond is the way that metal atoms are kept together within a metal material. If atoms have similar electronegativities (the. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond?
1.6 Periodic Variations in Element Properties Chemistry for
Web mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond similar to a covalent bond. However, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) a lead is malleable, so it can be pounded into flat sheets..
Why Do Most Atoms Form Chemical Bonds? Sciencing
Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. The mercurous ion also exhibits metallic and covalent. Its bonds are formed by large differences in electronegativity. A kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons. Web for example, covalently bonded gallium atoms tend to form crystal structures that are held together via metallic bonds.
What Is Metallic Bonding Metallic Bonding and Structure YouTube
Web aluminum atom is most likely to form a metallic bond. The loss of metallic properties b. Its bonds are formed by large differences in electronegativity. It has only metallic bonds between the atoms. Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond get the answers you need, now!
Chemistry B.Sc Level How many types of chemical bond
Which is most likely the result of millions of metal atoms crowding together so that molecular orbitals become combined? Web mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) aluminum (al) is most likely to form a metallic bond. Web which atom is most likely to.
Metallic Bonding Meaning, Properties, Factors Embibe
Web aluminum atom is most likely to form a metallic bond. If atoms have similar electronegativities (the. Web for example, covalently bonded gallium atoms tend to form crystal structures that are held together via metallic bonds. Ionic bonding results from the electrostatic attraction of oppositely. A kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons.
Web For Example, Covalently Bonded Gallium Atoms Tend To Form Crystal Structures That Are Held Together Via Metallic Bonds.
Metallic bonds are the kind of bonds that forms between metallic atoms. The loss of metallic properties b. Web when one atom takes an electron away from another and the resulting positive and negative ions are attracted to each other, those atoms have formed an ionic bond. Web mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper.
A Metallic Bond Is A Type Of Chemical Bond Similar To A Covalent Bond.
Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? A kind of chemical bonding which generates between conduction electrons. Define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds. It has only covalent bonds between the atoms.
Because Metals Are Solid, Their Atoms Are Tightly Packed In A Regular.
Which is most likely the result of millions of metal atoms crowding together so that molecular orbitals become combined? Web describe the formation of covalent bonds. Aluminium (al) atom is most likely to form a metallic bond. Web this bonding occurs primarily between nonmetals;
Its Bonds Are Formed By Large Differences In Electronegativity.
Web which atom is most likely to form a metallic bond? However, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. Aluminum (al) helium (he) phosphorus (p) carbon (c) aluminum (al) is most likely to form a metallic bond. Ionic bonding results from the electrostatic attraction of oppositely.



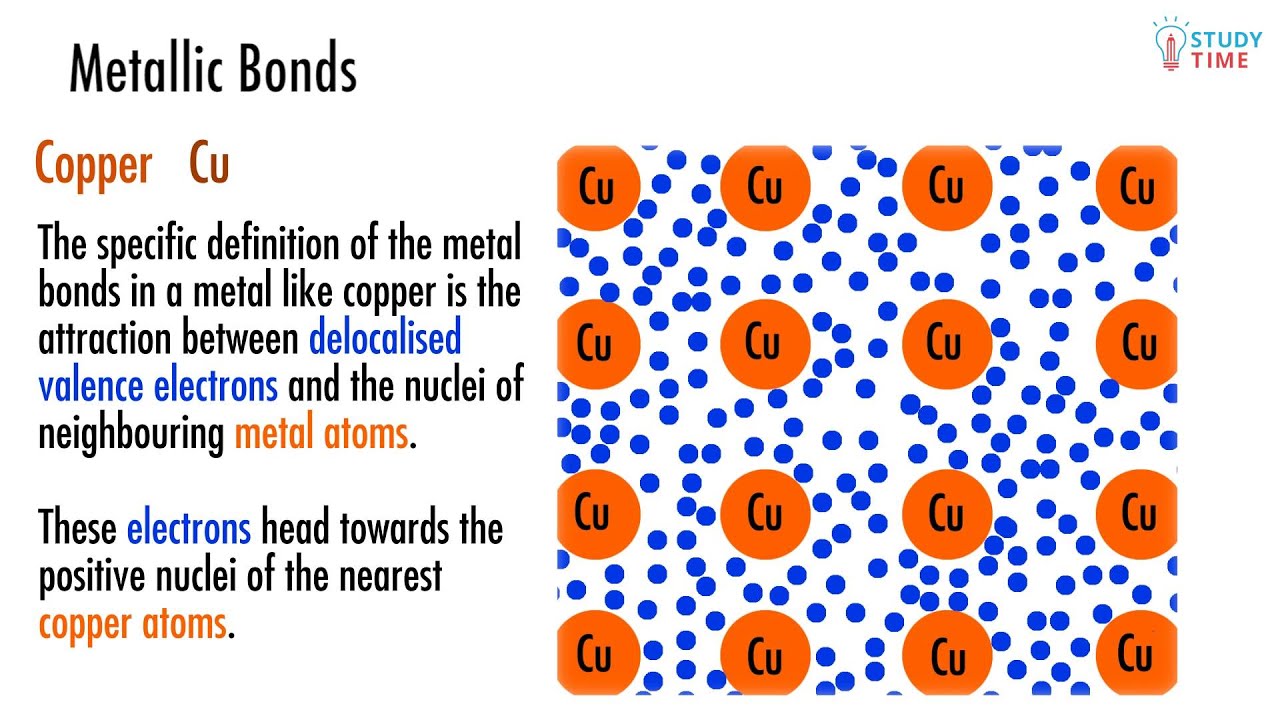


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/artwork-of-a-graphene-sheet-685024423-5c49e1cdc9e77c0001b8e3e9.jpg)